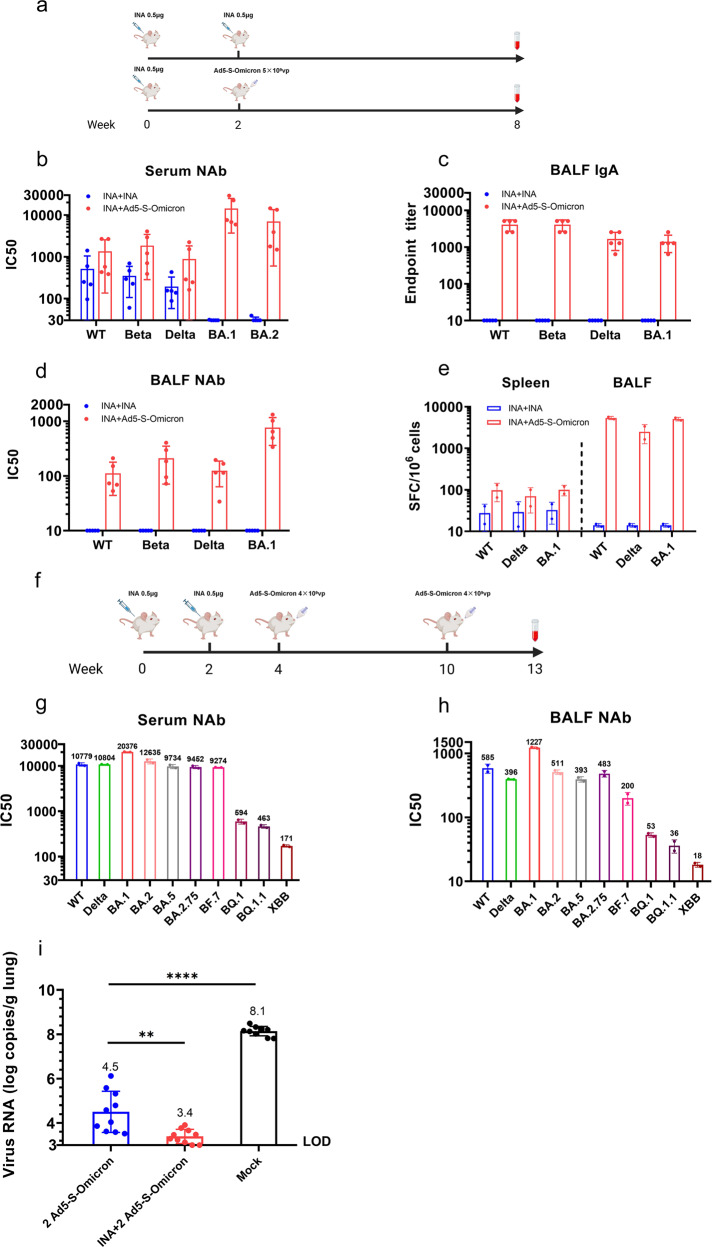
Fig. 2.
Intranasal Ad5-S-Omicron on the basis of inactivated vaccine establishes broad mucosal and systemic immunity and confers protection in mice. a Schematic diagram of immunization regimens. Female 7-week-old BALB/c mice were vaccinated with inactivated vaccine (INA) (0.5 μg, 1/10 of human dosage). Two weeks later, mice received either one homologous boost with 0.5 μg INA or one heterologous intranasal boost with Ad5-S-Omicron (5 × 109 vp). At 6 weeks after the booster vaccination, serum, spleen, and BALF samples were collected for analysis. Serum (b) and BALF (d) pseudovirus NAb titers against Wildtype, Beta, Delta, Omicron BA.1, and BA.2. Data are shown as the means ± SD (n = 5). Individual data are presented. c Wildtype, Beta, Delta, and Omicron BA.1 spike-specific IgA antibody endpoint titers in BALFs. Data are shown as the means ± SD (n = 5), and individual data are presented. e IFN-γ ELISpot assay to measure the T cell immune response. Spleen or BALF cells from each group of 5 mice were isolated and pooled and incubated with spike peptide pools of Wildtype, Delta, and Omicron BA.1 for the detection of antigen-specific IFN-γ-secreting cells in duplicate. f Schematic diagram of vaccination regimens. Female 7-week-old BALB/c mice were vaccinated with 2 intramuscular injections of 0.5 μg inactivated vaccine (INA) and 2 intranasal boosts of 4 × 109 vp Ad5-S-Omicron. Three weeks after the last booster vaccination, serum and BALF samples were collected for analysis. g–h Serum (g) or BALF (h) samples from each group of 5 mice were pooled in equal volume for the neutralization assay in duplicate. Pseudovirus neutralizing antibody titers against Wildtype, Delta, Omicron BA.1, BA.2, BA.5, BA2.75, BF.7, BQ.1, BQ.1.1, and XBB. i Female 7-week-old hACE2 transgenic mice were divided into 3 groups (10 mice per group): (1) two doses of intranasal Ad5-S-Omicron (4 × 109 vp) at 2-week intervals; (2) two doses of intranasal Ad5-S-Omicron after vaccination with inactivated vaccine at 2-week intervals; and (3) mice without vaccination as control group. At 14 weeks after the initial vaccination, mice were challenged with intranasal instillation of 50,000 FFU Omicron BA.2.3. Three days later, mice were sacrificed and the lungs were collected for quantification of viral RNA using qPCR. Data are shown as the means ± SD (n = 10) and were analyzed with an unpaired t test (**P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001). Individual data are presented. Mice without vaccination showed no neutralizing titers over 1:10; thus, the data were not presented