Figure 4. RNA–DNA hybrids mediate heterochromatin formation in centromeric repeats in HeLa and mouse ESC.
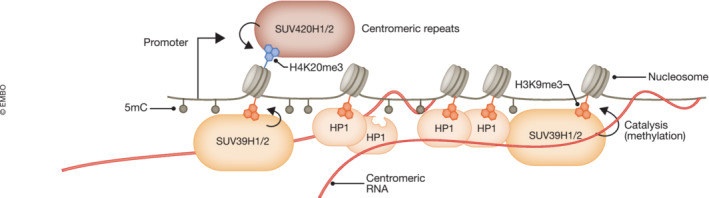
Deposition of H3K9me2/3 is involved in heterochromatin formation and transcriptional repression especially at repetitive elements (Bannister et al, 2001). Chromatin‐associated RNAs produced by centromeric α‐satellite repeats, remain in cis at the transcription site and act as platforms for stable association of SUV39 histone methyltransferase enzymes (Johnson et al, 2017; Velazquez Camacho et al, 2017). Particularly, the chromodomain of SUV39H1, which recognizes H3K9me2/3, has an intrinsic RNA and DNA binding affinity and promotes its centromeric localization (Shirai et al, 2017). Additional chromodomain‐containing proteins such as HP1, which can also bind to RNA, H3K9me2/3 (Muchardt et al, 2002), and SUV39 histone methyltransferases (Yamamoto & Sonoda, 2003) are recruited at the site and mediate chromatin compaction.
