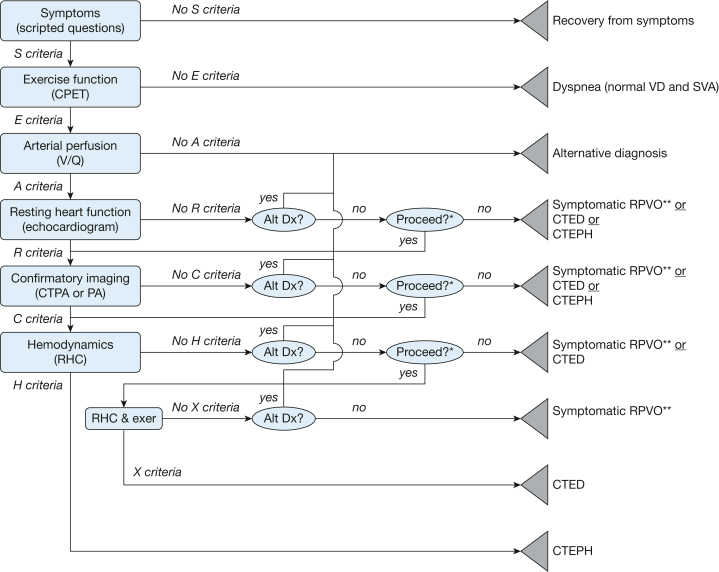
Figure 1.
SEARCH (symptom screen, exercise function, arterial perfusion, resting heart function, confirmatory imaging, and hemodynamics) algorithm decision tree.
The SEARCH algorithm grades potential outcomes after pulmonary embolism into distinct, nonoverlapping diagnostic categories. Rectangles represent criteria-driven nodes that reflect dichotomous objective test results. The ovals represent subjective clinical decision nodes. The triangles represent endpoint nodes that reflect the specific differential diagnoses warranted from the clinical data. Alt Dx = alternative diagnosis; CPET = cardiopulmonary exercise testing; CTED = chronic thromboembolic disease (pulmonary hypertension with exercise); CTEPH = chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; CTPA = CT pulmonary arteriogram; exer = exercise; PA = pulmonary arteriogram; SVA = stroke volume augmentation during exercise; symptomatic RPVO = symptomatic residual pulmonary vascular occlusion; VD = physiologic dead space ventilation; X Criteria = pattern of findings during exercise right heart catheterization.
∗The choice to proceed will depend on the clinical importance of distinguishing among the remaining diagnostic possibilities (eg, symptomatic residual pulmonary vascular occlusion vs chronic thromboembolic disease (pulmonary hypertension with exercise vs chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension) in the patient being evaluated. ∗∗Symptomatic residual pulmonary vascular occlusion is subtyped as chronic thromboembolic disease with increased physiologic dead space ventilation, chronic thromboembolic disease with decreased stroke volume augmentation, chronic thromboembolic disease with increased physiologic dead space ventilation and decreased stroke volume augmentation, or chronic thromboembolic disease with unspecified physiologic effect. S, E, A, R, C, and H criteria represent prespecified test results, as described in the text.