FIGURE 2.
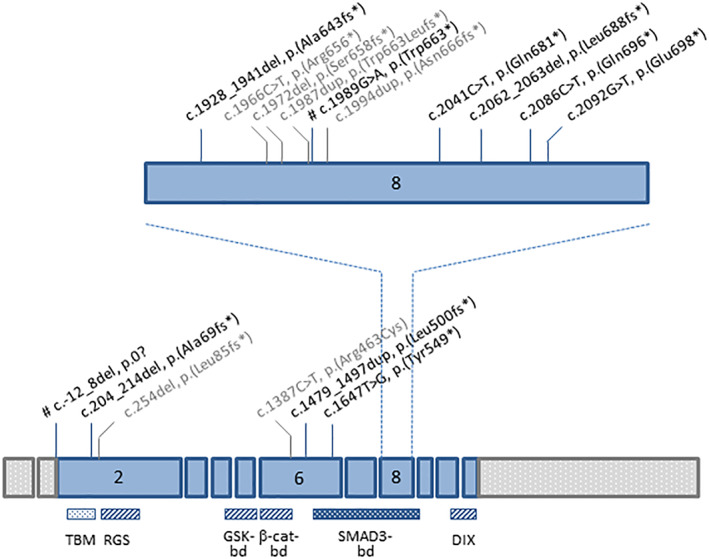
Genomic structure of AXIN2 gene showing the location of variants associated to colorectal adenomatous polyposis or CRC. Boxes represent exons. Pathogenic/likely pathogenic AXIN2 variants described in this study are indicated in black. All were novel, except two (marked by #). 10 , 21 Variants which were described in other studies are indicated in gray. 9 , 11 , 12 , 13 , 14 , 15 Functional domains of AXIN2 protein are shown below. 4 , 22 , 23 , 24 TBM, tankyrase‐binding motifs (role in regulation of AXIN2 stability); 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 RGS, regulator of G‐protein signaling (APC‐binding domain); GSK‐bd, glycogen synthase kinase 3β‐binding domain; β‐cat‐bd, β‐catenin‐binding domain; 4 SMAD3‐bd, SMAD3‐binding domain; 4 , 24 DIX, Disheveled and Axin (Disheveled‐binding domain and Axin homodimerisation). 4
