Figure 4.
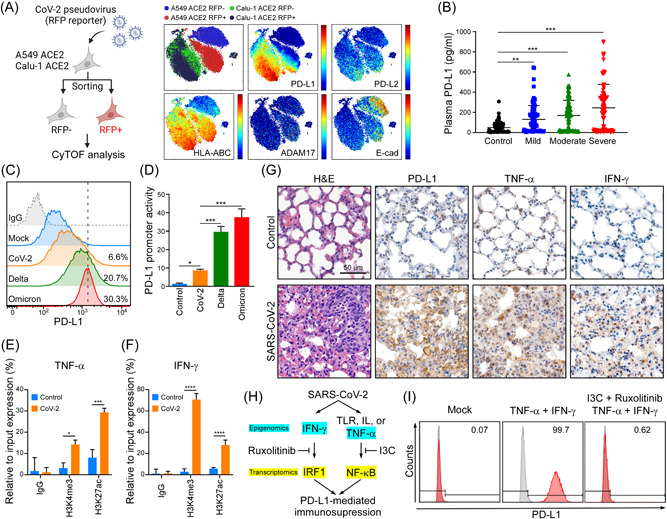
SARS‐CoV‐2 induces PD‐L1 through TNF‐α/IFN mediated NF‐κB/IRF1 axis. (A) CyTOF analysis of PD‐L1, PD‐L2, HLA‐ABC, ADAM17, and E‐cad in A549‐hACE2 and Calu‐1 ACE2 upon SARS‐CoV‐2 pseudovirus infection. (B) ELISA detection of the indicated group's plasma samples binding to precoated PD‐1. Data shown are means ± SD from control (n = 60), mild (n = 48), moderate (n = 59), and severe (n = 54) patients. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (one‐way ANOVA). (C) Flow cytometry analysis of PD‐L1 in A549‐hACE2 cells upon SARS‐CoV‐2, and Omicron pseudovirus infection. (D) Promoter‐luciferase reporter activity of PD‐L1 (−373/+328) by infection of SARS‐CoV‐2, and Omicron pseudovirus. Statistical method: one‐way ANOVA, Tukey post hoc tests, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001. (E, F) ChIP analysis of enrichment of H3K4me3 and H3K27ac modification in TNF‐α (E) and IFN‐γ (F) promoters after SARS‐CoV‐2 infection in A549‐hACE2 cells for 1 day. The enrichment levels were analyzed by RT‐qPCR and shown as the percentage of input. Statistical method: two‐way ANOVA, Tukey post hoc tests, *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001 (n = 3 with mean ± SD shown). (G) Representative data of immunohistochemistry staining of TNF‐α and IFN‐γ in lung tissues of SARS‐CoV‐2 infected AAV‐hACE2 mice at 5 dpi. Scale bar = 50 µm. (H) Schematic diagram of SARS‐CoV‐2 induces PD‐L1‐mediated immunosuppression through NF‐κB/IRF1 axis. (I) Flow cytometry was performed to detect surface PD‐L1 protein expression. A549 cells were pretreated with I3C and Ruxolitinib for 1 h, following by treating with 10 ng/ml TNF‐α and 10 ng/ml IFN‐γ for 48 h. AAV‐hACE2, adeno associated virus‐human angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2; ANOVA, analysis of variance; IFN‐γ, interferon‐γ; IRF1, interferon regulatory factor 1; NF‐κB, nuclear factor‐κB; PD‐1, programmed cell death protein 1; PD‐L1, programmed death ligand‐1; SARS‐CoV‐2, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; RT‐qPCR, real‐time quantitative polymerase chain reaction; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor‐α.
