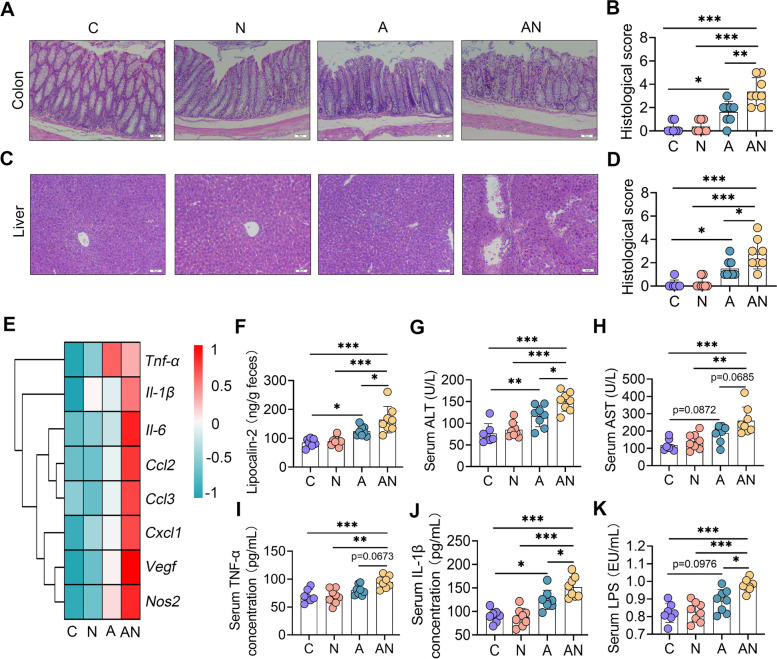
Fig. 4.
Sialic acid facilitates gut dysbiosis-induced mucosal and systemic immune imbalance in mice. A Representative H&E-stained colon sections from the indicated mice (scale bar, 50 μm). B Histological score of colons from different treatment groups (n = 7–8). C Representative H&E-stained liver sections from different groups (scale bar, 50 μm). D Histological scores of the livers based on H&E staining (n = 7–8). E Colon mRNA levels from the indicated mice as assessed by qPCR (n = 7–8). F Fecal lipocalin-2 levels were assessed to validate mucosal inflammatory responses (n = 7–8). Serum ALT (G) and AST (H) levels were determined to assess liver injury (n = 7–8). Levels of serum TNF-α (I), IL-1β (J), and LPS (K) showed the systemic inflammatory responses caused by gut dysbiosis and sialic acid treatment (n = 7–8). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (B, D, and F–K) and one-way ANOVA was performed, followed by Tukey test (B, D, and F–K). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 indicate significant difference