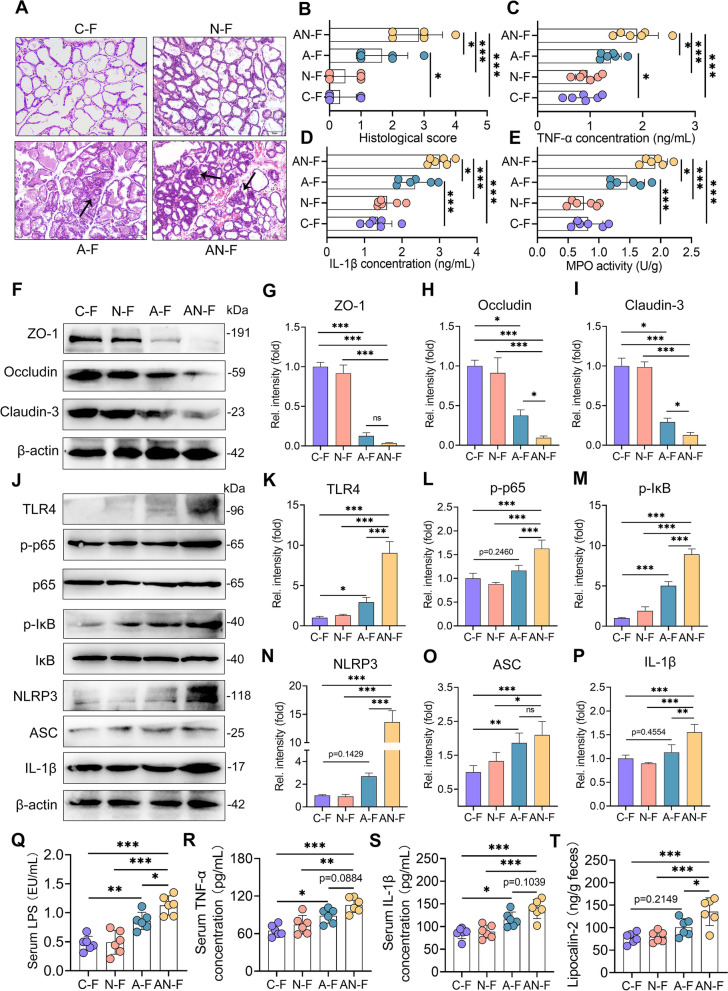
Fig. 8.
FMT from AN group mice induces mastitis in recipient mice. A Representative images of H&E-stained sections from different FMT groups (scale bar, 50 μm). Arrows indicate inflammatory infiltration. B The histological scores of mammary glands from the different FMT groups (n = 6). The proinflammatory markers TNF-α (C) and IL-1β (D) and MPO activity (E) were measured (n = 6). F Representative images of ZO-1, Occludin, and Claudin-3 in mammary glands from the indicated mice. The intensities of ZO-1, Occludin, and Claudin-3 were determined (G–I) (n = 4). J The protein levels of the TLR4-NF-κB/NLRP3 pathways in the mammary gland were assessed by western blotting. The relative intensities of TLR4, p-p65, p-IκB, NLRP3, ASC, and IL-1β in the mammary gland were determined (K–P) (n = 4). Serum LPS (Q), TNF-α (R), IL-1β (S), and fecal lipocalin-2 (T) were determined (n = 6). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (B–E, G–I, K–P, and Q–T) and one-way ANOVA was performed, followed by Tukey test (B–E, G–I, K–P, and Q–T). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 indicate significant difference