Figure 5.
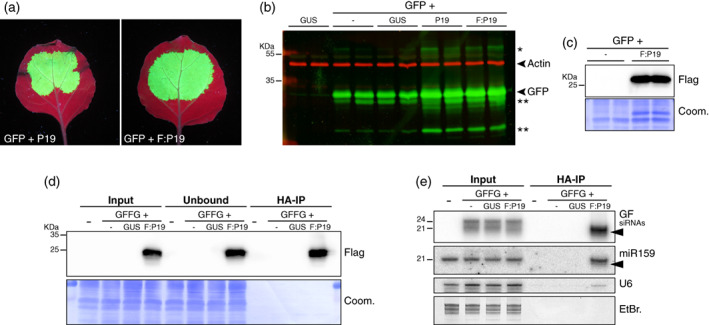
P19 selectively binds the 21‐nt siRNAs produced in infiltrated patches during IR‐PTGS. (a) Images of Nicotiana benthamiana leaves, representative of six independent experiments, at 4 dpi with the constructs p35S::GFP5 (GFP), p35S::P19 (P19), and p35S::FHA:P19 (F:P19), as indicated, under UV illumination.
(b) GFP protein accumulation (green signal) in biological duplicates of the samples depicted in (a) and their controls (p35S::FHA:GUS‐Intron: GUS), analyzed by Western blot. An anti‐actin antibody was used to provide a control for equal protein loading (red signal). *Indicates higher‐molecular‐weight forms of the GFP protein or potential concatemers thereof. **Indicates truncated byproducts of the GFP protein. The experiment was independently repeated three times with similar results.
(c) FHA:P19 protein levels in biological duplicates of one of the samples depicted in (a) and its controls analyzed by Western blot. Coomassie staining of total proteins (Coom.) provides a control for equal loading. The experiment was independently repeated three times with similar results.
(d) FHA:P19 protein levels in the input, unbound fraction, and IP fraction of N. benthamiana leaves at 4 dpi with infiltration medium (−), p35S::FHA:GUS‐Intron (GUS), p35S::FHA:P19 (F:P19), and p35S::GFFG (GFFG), as indicated. Coom.: as in (c). The experiment was independently repeated four times with similar results.
(e) GF siRNAs levels in samples depicted in (d) analyzed by Northern blot. miR159 and U6 small RNA were used as an endogenous P19 cargo and RNA loading control, respectively. EtBr.: Ethidium bromide staining provides an additional RNA loading control. Black arrows indicate 3′‐end‐trimmed sRNA species. The experiment was independently repeated four times with similar results.
