Figure 1.
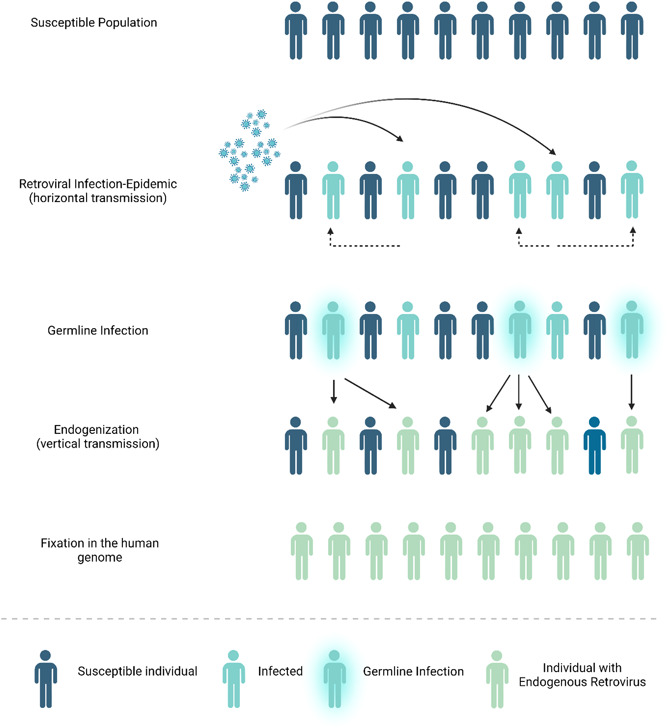
HERV life cycle. HERVS are viral sequences integrated into the human genome, resulting from multiple invasion events of ancient exogenous retroviruses, after their horizontal transmission and the occurrence of retroviral epidemics. Endogenization occurred after the infection of germ‐line cells and subsequent vertical transmission, and these elements either became extinct or reached fixation in the human genome, HERVs are vertically transmitted via Mendelian inheritance and are found scattered throughout the host's genome.
HERVs, human endogenous retroviruses.
