Figure 3.
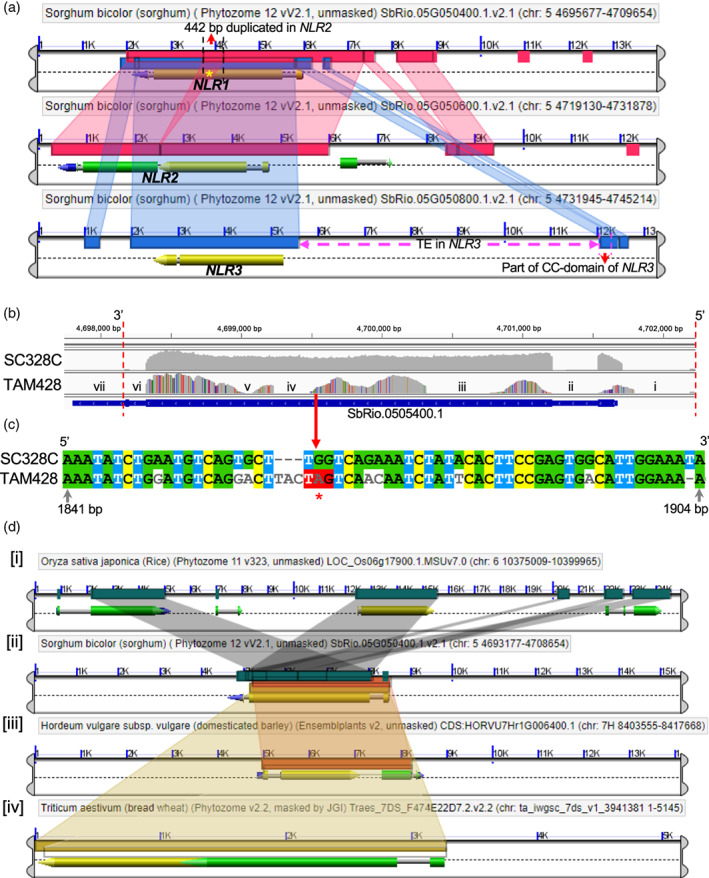
Comparative genomics (CoGe) of ARG2 duplicate genes and sequence variation of ARG2 in parental lines.
(a) CoGe view of the three duplicate NLR genes in the ARG2 mapping interval using the Rio reference genome. The three panels show the three duplicate genes, and the colored connectors between the panels show homologous segments. NLR2 (in the middle panel) was predicted as two genes (SbRio.05G050500 and SbRio.05G050600), although these two putative genes are parts of a single gene and code for a single transcript. The dark green overlapping connector between NLR1 and NLR2 (marked with asterisk) shows a 442‐bp segment of NLR1 that is a duplicate in NLR2. The bottom panel shows a big transposon insertion (TE in NLR3) that disrupted the upstream gene region of NLR3.
(b) The integrated genomic view (igv) of NLR1 transcript raw‐reads of the parental lines of ARG2 mapping population that are aligned to the Rio reference genome. These sequences were obtained using WideSeq. The numbers on top are genomic coordinates of ARG2. The vertical distance of the gray area shows the depth of aligned reads, which ranges from 700 to > 7000. The uniformly gray area shows that aligned reads of SC328C are identical to the reference genome, and the SNPs in TAM428 are shown by red, orange, blue and purple vertical lines in the gray background. The gene regions in the TAM428 panel that does not show aligned reads (no gray area) are (iv) a 62 bp indel and (iii and v) exon segments with dense SNPs that prohibited alignment. The remaining no‐gray regions (i, ii and vi) are intronic segments and (vii) part of the 3′ UTR that was not included in the sequencing. The gene structure (below the panels) is the putative NLR1 gene in the reference genome.
(c) Aligned coding sequences that carry the premature stop codon in the susceptible parent.
(d) A snapshot of the top ARG2 homologs in rice, barley and wheat that were identified using CoGe. The different color connectors between the panels show the homologous segment between genes in the different species. (i) O. sativa has a cluster of three highly homologous genes, one of them has gene ID LOC_Os06g17880 (Apoptic ATPase, LRR annotations similar to ARG2). (iii) H. vulgare (barley) homolog has the gene ID HORVU7Hr1G006400. (iv) The homology with top homolog in T. aestivum covers 99% peptide segment, gene ID Traes_7DS_9881A234E [RPM1, Apoptic ATPase, NB‐ARC, LRR annotations].
