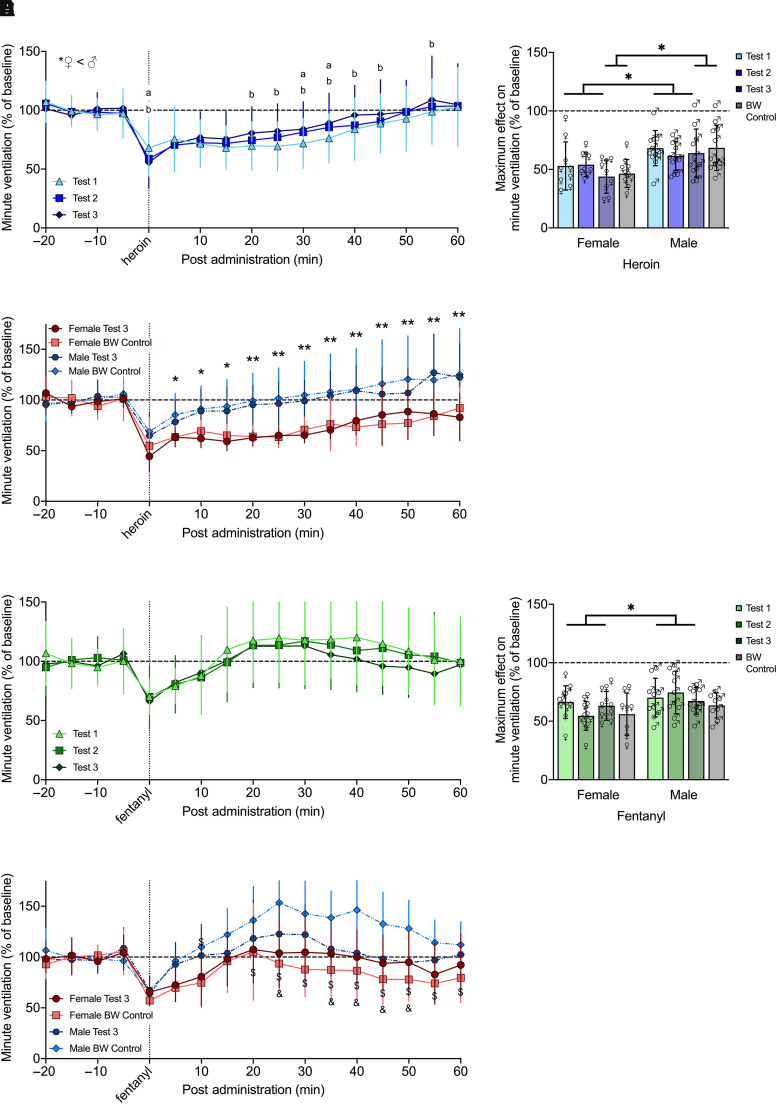
Fig. 4.
Effects of intermittent (2 to 3 weeks apart) acute administration of heroin or fentanyl on minute ventilation. Rats received i.v. injections (tests 1, 2, and 3) of heroin (600 µg/kg; n = 9 females, 11 males) or fentanyl (25 µg/kg; n = 11 females, 10 males) over 5 weeks. During test 3, a body-weight control group received heroin (n = 10 females, 12 males) or fentanyl (n = 8 females, 8 males). The rats exhibited minimal tolerance to heroin administered after several weeks, although the first dose induced greater decreases in minute ventilation at some of the later time points, and females had significantly greater decreases than males. aP < 0.05, test 1 versus test 2. bP < 0.05, test 1 versus test 3 (A). Heroin-induced maximal decrease in minute ventilation was significantly lower in females (∼50%) compared with males (∼65%) across test and age-matched groups. *P < 0.05, males versus females (B). For age-matched groups (test 3 versus body-weight control), females had significantly greater decreases than males, but there were no differences in the effects of heroin *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, males versus females (C). The rats exhibited no tolerance to fentanyl administered after several weeks, with no difference between males and females (D). Fentanyl-induced maximal decrease in minute ventilation was significantly lower in females (∼60%) compared with males (∼70%) across test; however, there was no difference between sexes for age-matched groups. *P < 0.05, males versus females (E). For age-matched groups, females had significantly greater decreases than males, driven by an overshoot in the male body-weight control group, which was higher than the control females and test 3 males at several of the later time points. $P < 0.05, control males versus females. &P < 0.05, control males versus test 3 males (F). Data are expressed as mean ± S.D. in percentage of baseline in 5-minute bins over −20 to 60 minutes postadministration (A, C, D and F) or lowest value within 25 minutes postadministration (B and E). Dashed line indicates average baseline measure. ♀, female; ♂, male; BW, body weight.