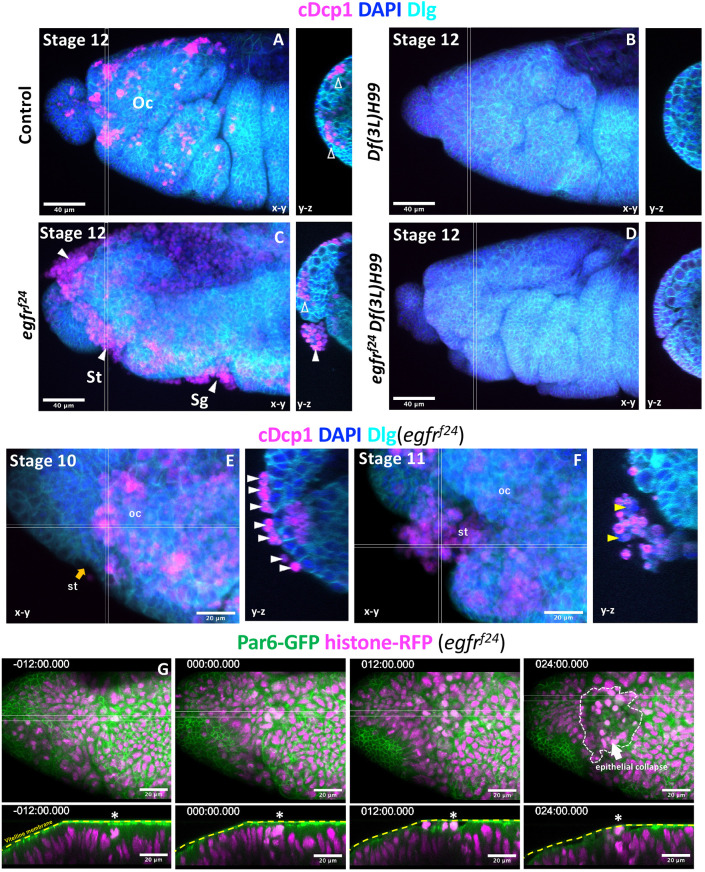
Fig. 3.
Apical extrusion of apoptotic and non-apoptotic cells in EGFR mutants. (A-F) Active caspase staining (cDcp1) of a control (A), a Df(3L)H99 mutant (B), an EGFR mutant (C,E,F) and an EGFR/Df(3L)H99 double mutant (D). More than 10 embryos of each genotype were examined, except for the EGFR/Df(3L)H99 double mutant (n=4). cDcp1-positive cells appeared as clusters within, or basal to, the plane of the epithelium (open arrowheads) of control embryos (A). In EGFR mutants, apoptotic cells appeared basal to the epithelium; however, most appeared apical to the epithelium (white arrowheads) (C). Apical cells were all cDcp1 positive at early stage 10 (E). At late stage 11, cDcp1-negative cells were found in the apical location (yellow arrowheads, F). (G) Live imaging of the head region of the EGFR mutant showing an extensive collapse in the ocular segment of the head (arrow in the 24 min panel). Here, t=0 was set at the time the first apical cell extrusion event was observed (asterisks). st, stomodeum; oc, ocular segment; sg, salivary gland. Orange arrow indicates the invagination region of ectoderms into the stomodeum.