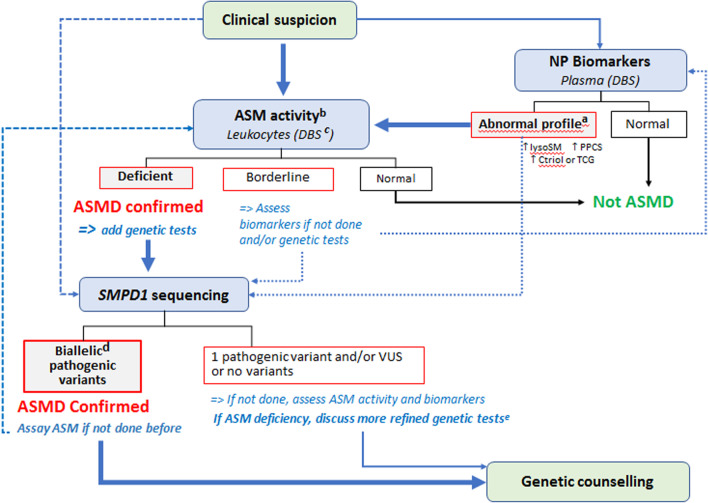
Fig. 1.
Algorithm for the laboratory diagnosis of ASMD. (a) Significant increase of 3β,5α,6β-cholestane-triol (C-triol), 7-ketocholesterol (7-KC), 3β,5α,6β-trihydroxy-cholanoyl-glycine (TCG), lysosphingomyelin (lyso-SM), N-palmitoyl-O-phosphocholine-serine (PPCS). A difference with an NPC profile is the normal or slightly elevated lyso-SM level in the latter. Other causes of elevated C-triol levels include cerebro tendinous xanthomatosis (CTX) and acid lipase deficiency. (b) LC–MS/MS (or radioisotopic) preferred methods (see Statement 13). (c) Recommendation for ASM in DBS to be confirmed on leukocytes or by genetic testing. (d) Importance of parental study. (e) MLPA/RNA analysis. VUS: Variant of uncertain significance