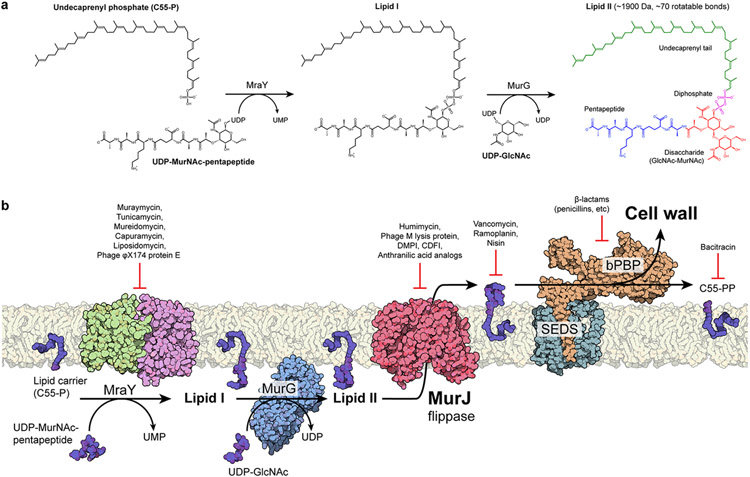
Figure 2.
Membrane-associated steps of peptidoglycan biosynthesis are hot spots for antibiotic targeting. (a) Soluble cell wall precursors are synthesized in the cytosol and attached to the lipid carrier C55-P by MraY and MurG to form the lipid-linked intermediate lipid II. Lipid II is a large (~1,900 Da), flexible (~70 rotatable bonds), and anionic molecule that requires a dedicated transport protein to flip across the membrane. (b) On the periplasmic side of the cell membrane, a series of glycosyltransferase (SEDS proteins) and transpeptidases (class B PBPs) activities form the cell wall. The flippase MurJ forms the critical link between the cytosolic and periplasmic steps by flipping lipid II from the cytoplasmic side to the periplasmic side. Many of these steps are established targets of known antibiotics.
Abbreviations: C55-P, undecaprenyl phosphate; C55-PP, undecaprenyl diphosphate; CDFI, 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-3- [1-(2,3-dimethylbenzyl)piperidin-4-yl]-5-fluoro-1H-indole; DMPI, 3-{1-[(2,3-Dimethylphenyl)methyl]piperidin-4-yl}-1-methyl-2- pyridin-4-yl-1H-indole; GlcNAc, N-acetylglucosamine; MurNAc, N-acetylmuramic acid; bPBP, class B penicillin-binding protein; SEDS, shape, elongation, division, sporulation; UDP, uridine diphosphate; UMP, uridine monophosphate.