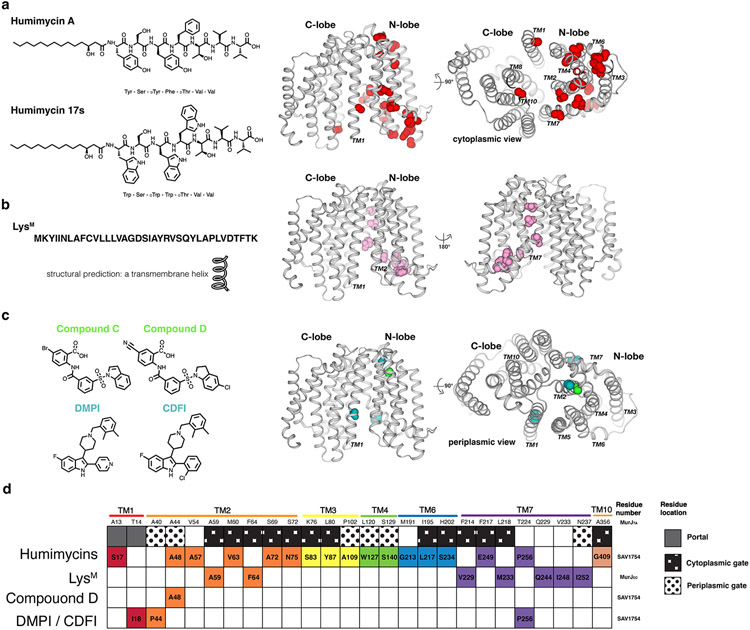
Figure 7.
Inhibitors of MurJ. (a) Chemical structures of humimycins. The locations of resistance mutations mapped to the MurJTA structure are indicated as spheres. (b) Peptide sequence of LysM and resistance mutations to LysM mapped to the MurJTA structure. (c) Chemical structures of the putative small-molecule inhibitors DMPI, CDFI, Compound C, and Compound D. Resistance mutations to each were mapped to the MurJTA structure. (d) A barcode tabular summary of resistance mutations for each inhibitor and their locations on MurJ. Humimycins appeared to target the portal and cytoplasmic gate of MurJ, while LysM putatively targets the TM2–TM7 region of MurJ facing outside, toward the membrane. The mechanism of small-molecule inhibitors is less clear due to the small number of resistant mutants that have been isolated.
Abbreviations: CDFI, 2-(2-Chlorophenyl)-3-[1-(2,3-dimethylbenzyl)piperidin-4-yl]-5-fluoro-1H-indole; DMPI, 3-{1-[(2,3-Dimethylphenyl)methyl]piperidin-4-yl}-1-methyl-2-pyridin-4-yl-1H-indole; LysM, phage M lysis protein; MurJTA, Thermosipho africanus MurJ; TM, transmembrane helix.