Figure 2. Tumor Microbiome at Gutdistal Sites.
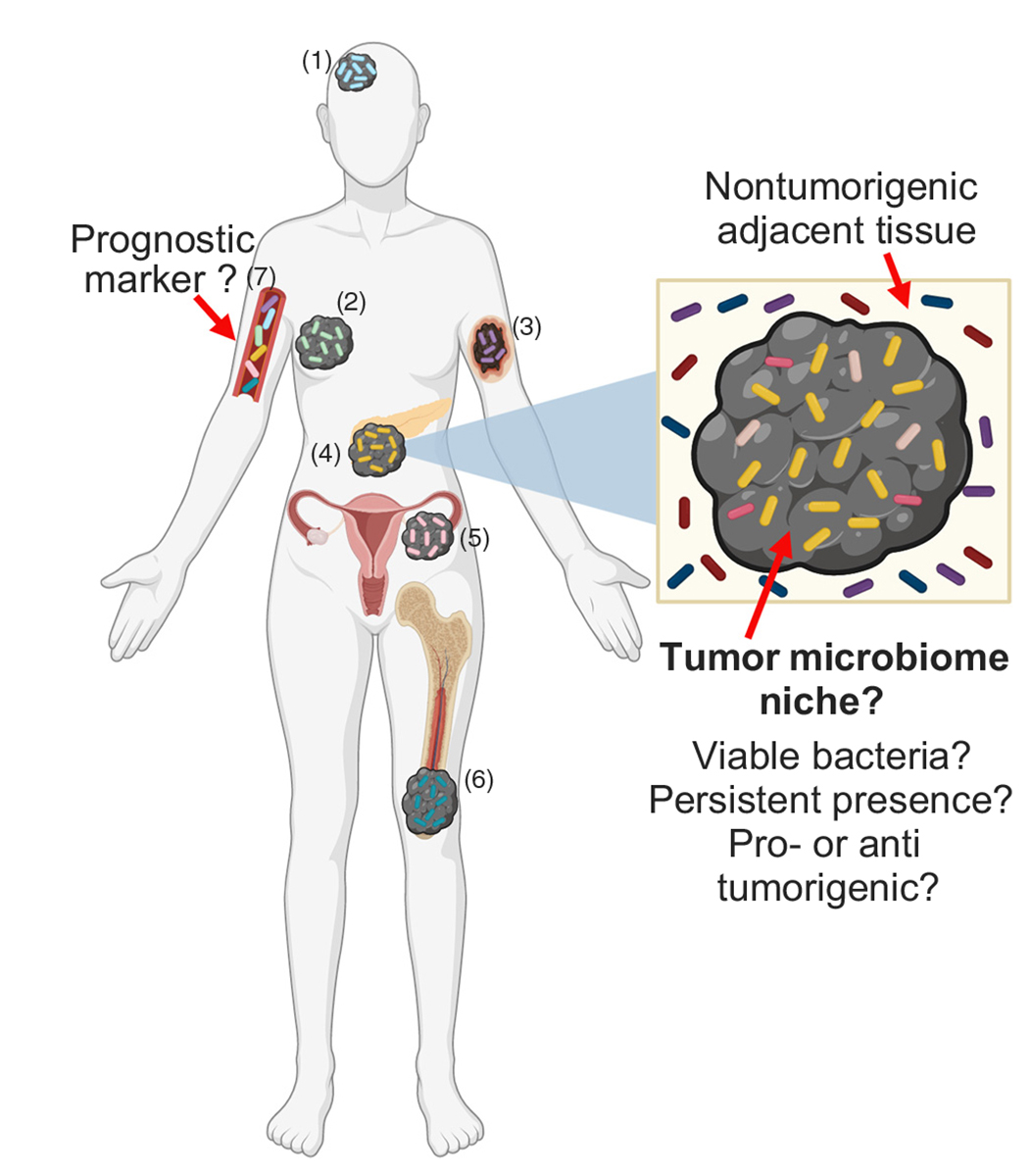
Gut-distal tumor types such as glioblastoma (1), breast (2), melanoma (3), pancreatic (4), ovarian (5), and bone (6) cancer provide a biological niche for specific bacterial growth [35–40]. These distinct human cancer-type-specific tumor microbiomes may provide a novel, powerful diagnostic marker for distinguishing between normal and cancerous tissue, as well as between specific cancer types via analysis of microbial signatures in the plasma (7) [38,39].
