Fig. 1. STARSS.
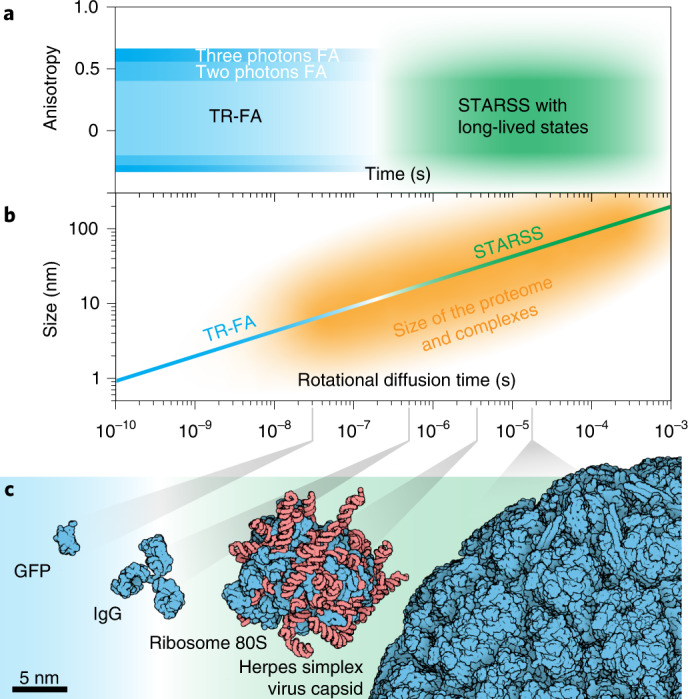
a, Anisotropy values and temporal regime accessible to conventional time-resolved anisotropy and STARSS. By continuously probing the same subset of molecules populating the same reversible switchable state, it is possible to extend the observable time window to microseconds and milliseconds. This previously inaccessible temporal regime enables measurement of slower rotational diffusion. b, STARSS can measure slower rotational diffusion coefficients and thereby quantify the mass and mass changes of large protein complexes, as well as complex dynamics, in a local viscous environment. The relationship between rotational diffusion time and the size of complexes is shown, together with the domain of applicability of techniques. c, Size of proteins and biological complexes that can be investigated with STARSS.
