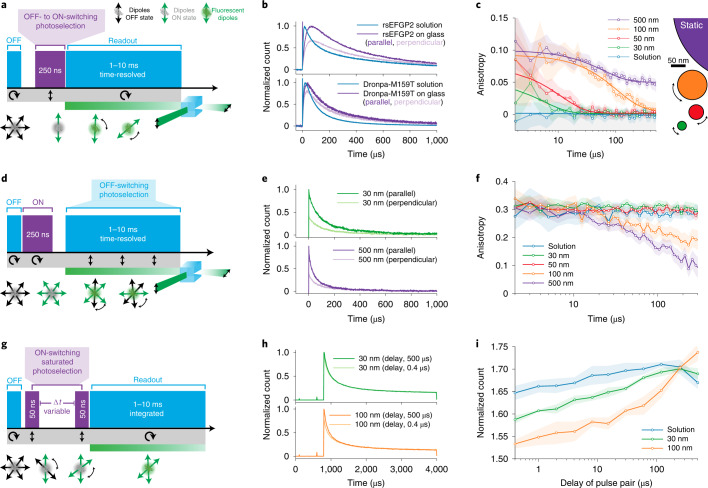
Fig. 2. STARSS with long-lived states in reversibly photoswitchable fluorescent proteins.
a, STARSS method 1 pulse scheme with photoselection during ON-switching, circular cyan light for probing and polarization-sensitive, two-channel detection. This methodology is the closest to typical TR-FA experiments. b, Experimental raw data recorded with STARSS method 1, showing distinct relaxation of the parallel and perpendicular channels for DronpaM159T and rsEGFP2 after ON-switching photoselection. c, STARSS method 1 experiments on beads of varying diameter. The logarithmic x axis shows the extended temporal observation window up to 500 µs, which allows measurement of tumbling of spheres of diameter 30–100 nm (500-nm beads are a reference static sample). Monoexponential fittings are shown, with parameters reported in Supplementary Information 3.2. d, STARSS method 2 pulse scheme with photoselection during OFF-switching, and with circular ON-switching and polarized-sensitive detection. e, Detected raw signal recorded with STARSS method 2 for beads of varying size, reporting the decay of parallel and perpendicular channels. f, STARSS method 2 experiments on beads of varying diameter. g, STARSS method 3 consists of photoselection with polarized ON-switching pulses delivered at two distinct time points and circular cyan light to read out the fluorescence detected with polarized-sensitive detection. h, Detected raw signal with STARSS method 3 under two delay conditions for beads of varying size. i, STARSS method 3 curve derived from beads of varying size. The information on rotational diffusion is encoded in the increase in count for different delays between ON-switching pulses. Counts are normalized by the signal obtained from a scheme with a single ON-switching pulse. Shaded regions of anisotropy values are 95% confidence intervals evaluated from detector noise (Supplementary Information 20).