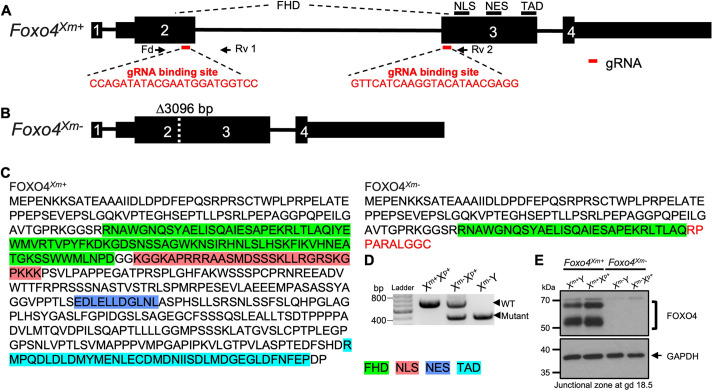
Fig. 5.
In vivo genome editing of the rat Foxo4 locus. (A) Schematic of the rat Foxo4 gene (Foxo4Xm+) and guide RNA target sites within exons 2 and 3 (NM_001106943.1). Black boxes represent exons, and red bars beneath exons 2 and 3 correspond to the 5′ and 3′ guide RNAs used in the genome editing. (B) The mutant Foxo4 allele (Foxo4Xm−) possesses a 3096 bp deletion. Parts of exons 2 and 3 are deleted, leading to a frameshift and premature stop codon in exon 3. (C) Amino acid sequences for FOXO4Xm+ and FOXO4Xm−. The red sequence corresponds to the frameshift in exon 3. The green, red, dark blue and light blue highlighted amino acid sequence regions correspond to the forkhead winged-helix DNA-binding domain (FHD), nuclear localization sequence (NLS), nuclear export sequence (NES) and transactivation domain (TAD), respectively. (D) Heterozygous mutant female rats were crossed to wild-type male rats to generate hemizygous null male rats. Wild-type (+/+; WT), heterozygous (+/−) and hemizygous null (−/y) genotypes were detected by PCR. (E) Western blot analysis of FOXO4 protein in the junctional zone of Foxo4Xm+ (Xm+Y and Xm+Xp+) and Foxo4Xm− (Xm−Y and Xm−Xp+) placentas at gd 18.5. GAPDH was used as a loading control.