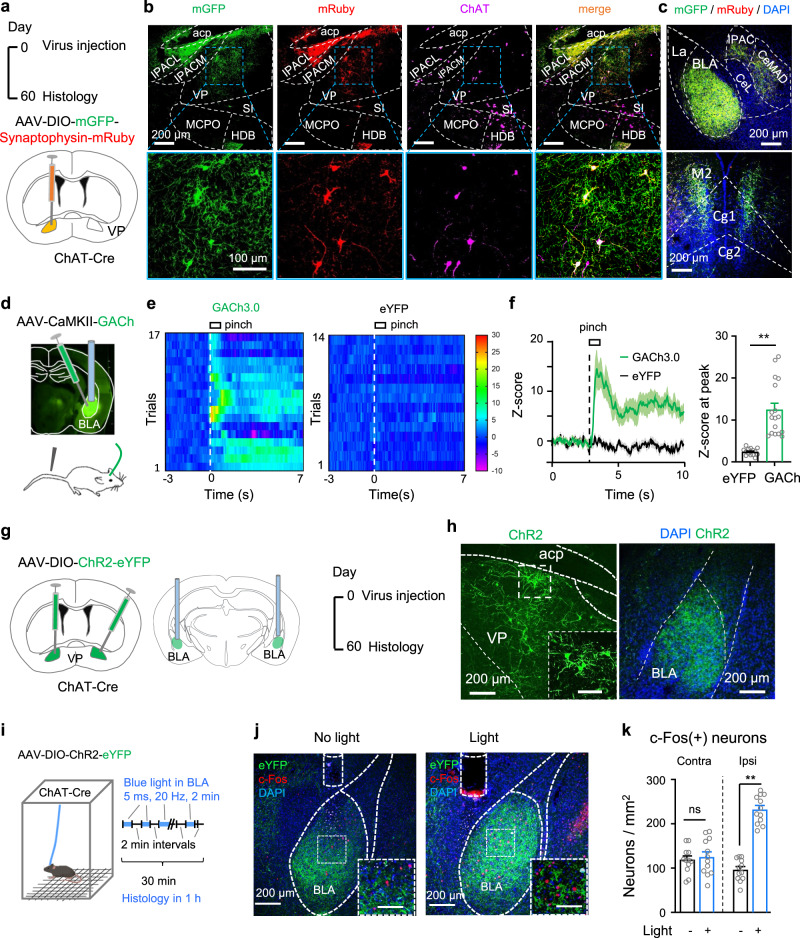
Fig. 8. VP ChAT neurons innervate BLA neurons via functional connections.
a AAV-EF1α-DIO-mGFP-Synpatophysin-mRuby was injected into the VP of ChAT-Cre mice. The mice were sacrificed 2 months later. b Histological verification of mGFP and mRuby in VP ChAT neurons. c mGFP and mRuby were colocalized in the BLA, the medial central amygdala (CeM), the cingulate cortex (Cg), and the secondary motor cortex (M2). d AAV-CaMKII-GACh, an ACh sensor, and AAV-hSyn-eYFP were transfected into the BLA in mice. Fiber photometry recordings were performed to monitor ACh release in the BLA. e, f GACh and eYFP signals in the BLA were transformed into z-scores. Heat-maps, summarized traces, and summary of the amplitudes of GACh and eYFP signals in response to a 1 s tail pinch are shown. Peak amplitudes: t = 5.683, df = 32, P < 0.0001, n = 17 trials from 6 GACh mice, n = 17 trials from six eYFP mice, two-tailed t-test. g AAV-EF1α-DIO-ChR2-eYFP was transfected in the VP of ChAT-Cre mice. h Representative images showing ChR2-expressing neurons in the VP and dense ChR2-expressing axonal fibers in the BLA. i AAV-EF1α-DIO-ChR2-eYFP was transfected into the right VP of ChAT-Cre mice and an optical fiber was implanted in the right BLA. Two-minute blue light stimulation (5 ms, 20 Hz, 4 mW) episodes with 2 min inter-episode intervals were delivered into the BLA for 30 min. The mice were sacrificed 1 h after stimulation for histological experiments. j Representative images showing that 30 min optogenetic stimulation of the VPChAT-BLA projection increased the number of c-Fos-positive neurons in the BLA. k c-Fos-positive neurons in the BLA in both hemispheres in mice with and without light illumination. Contralteral: t = 0.47, df = 22, P = 0.64. Ipsilateral: t = 11.87, df = 22, P < 0.0001. n = 12 slices from five mice, two-tailed t-test. **P < 0.01; ns not significant. Contra contralateral, Ipsi ipsilateral. Scale bar in (h, j): 100 μm.