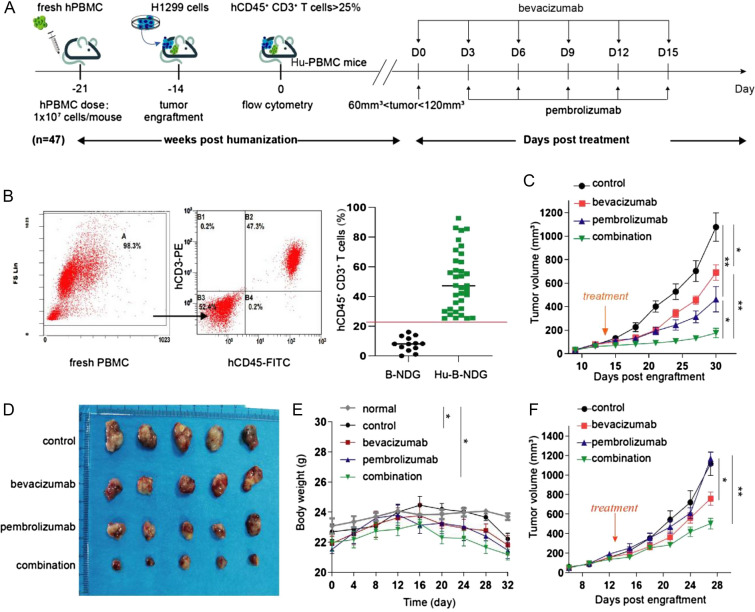
Fig. 1.
Efficacy of combined bevacizumab and pembrolizumab therapy in humanized mouse models of non-small cell lung cancer. a Schematic diagram of the construction and treatment of humanized mice. Adult B-NDG mice were injected with peripheral blood mononuclear cells intravenously, followed by subcutaneous transplantation of tumor cell lines. When the tumor reaches the therapeutic volume, the mice were randomly assigned to each treatment group. b The level of human CD45+CD3+ T cells in the blood of mice was monitored with flow cytometry, and the mice with a reconstruction level higher than 25% were selected for follow-up experiments. c Tumor growth curves of humanized mice bearing H1299 cells in the control, bevacizumab monotherapy, pembrolizumab monotherapy, and combination therapy groups. Arrow indicates start of treatment. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). *P < 0.05, and **P < 0.01. d At the end of treatment, the tumors were collected and photographed. e The body weight of the mice in each treatment group and normal B-NDG with no PBMCs transplantation was monitored every 4 days from the beginning of peripheral blood mononuclear cell transplantation to the end of treatment (n = 5). *P < 0.05. f Tumor growth curves of humanized mice bearing A549 cells in each of the four treatment groups after transplanted with PBMCs. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 5). *P < 0.05, and **P < 0.01