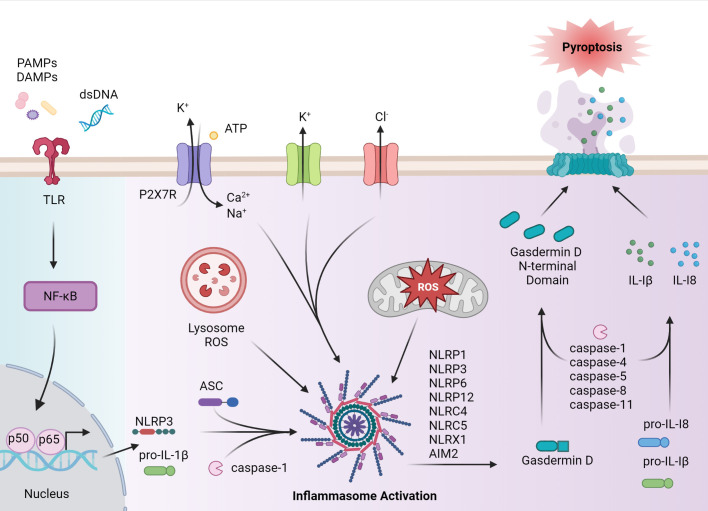
Figure 1.
Inflammasome assembly and activation. Canonical activation of the inflammasome pathway begins with a primary signal, such as PAMPs, endogenous-derived DAMPs, or dsDNA, that are recognized by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), such as toll-like receptors (TLRs). PRR activation induces NF-κB and subsequent expression of NLRP, pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18, and post-translational events. Formation of the inflammasome complex occurs when the sensor protein, such as NLRP3, binds to ASC, driving caspase activation and inflammasome assembly. Caspase enzymes cleave pro-IL-1β and pro-IL-18 as well as the C terminus from gasdermin D, allowing the gasdermin D N-terminal domain to form pores necessary for pyroptosis. IL-1β and IL-18, as well as cellular contents are released to establish a proinflammatory response. In autoimmune disease, inflammasome activation can occur via activation in a noncanonical matter including agonist-induced ion flux and lysosomal and mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS). The figure was prepared using Biorender software licensed to the UNC Lineberger Comprehensive Cancer Center.