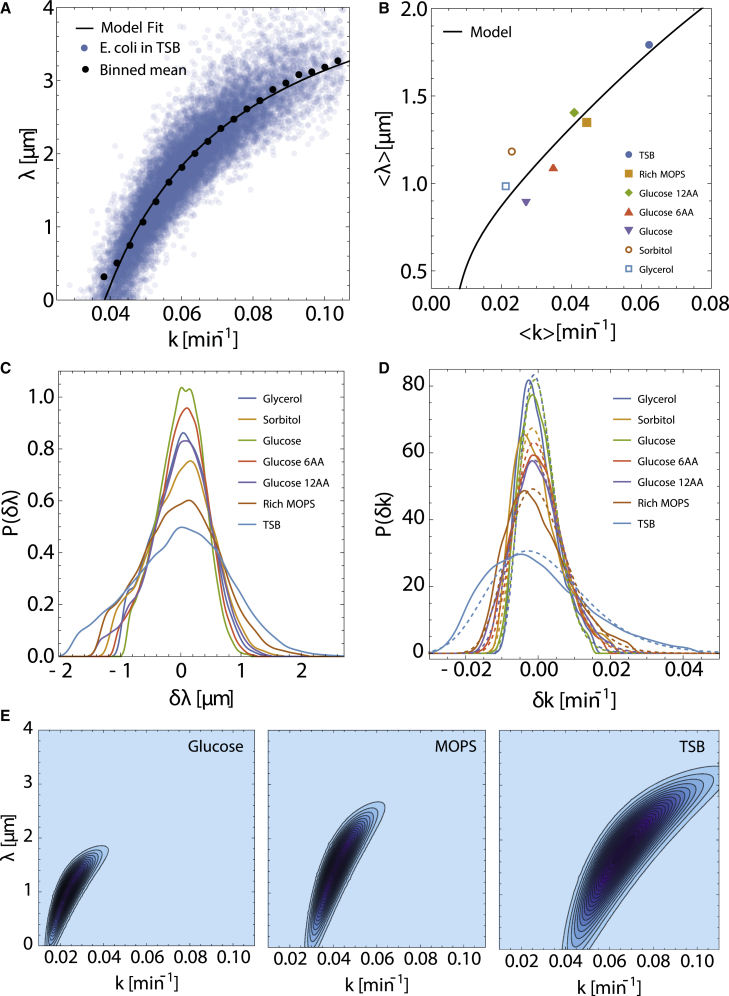
Figure 2.
Intergenerational fluctuations and correlations in E. coli cell growth parameters. (A) Scatterplot showing the correlation between k and λ obtained by fitting super-exponential growth model to E. coli cell length versus time data in TSB. The solid black curve represents a fit of Eq. 8 to the data. We remove outliers and the small number of generations in fast growth conditions with from further analysis (see materials and methods). (B) Ensemble-averaged versus across different growth conditions. The black curve is a model prediction for as a function of according to Eq. 9, with , , and . (C) Marginal probability distributions of across different growth conditions. (D) Marginal probability distributions of for each growth condition shown as solid color curves. Dashed curves of the same color depict fits of log-normal distributions. Experimental data presented in (A)–(D) are taken from (4). (E) Representative contour plots of the model predictions for the joint distribution , corresponding to mean growth rates in glucose, MOPS, and TSB media. Darker blue indicates higher probability. To see this figure in color, go online.