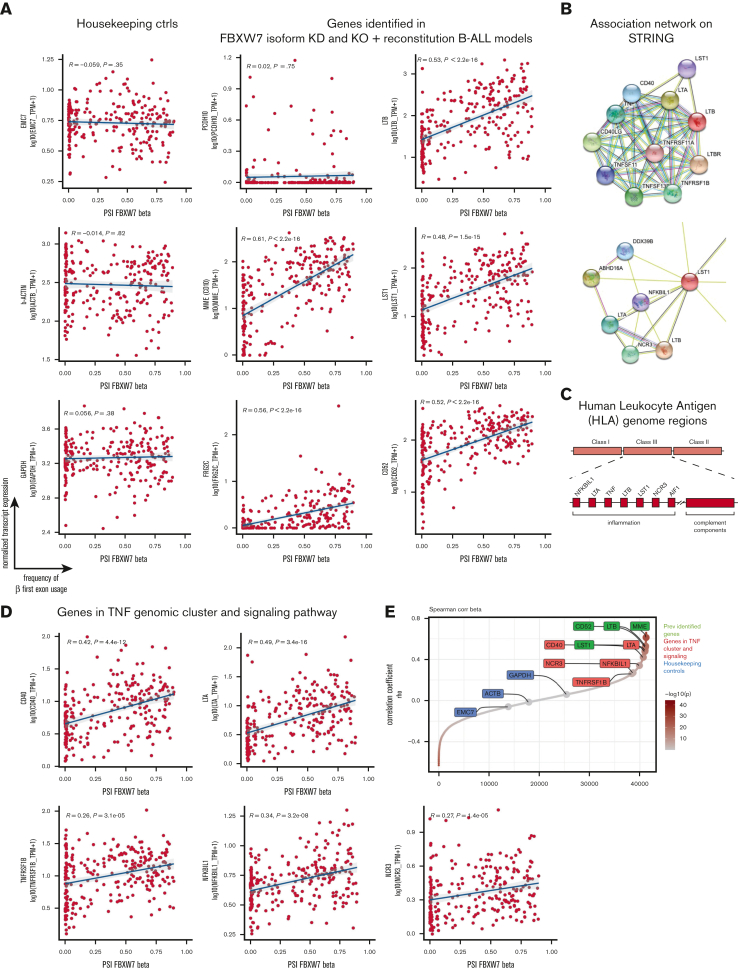
Figure 7.
Transcript expression of LTB, LST1, CD52, MME (CD10), and several members in the TNF superfamily pathway is positively correlated with FBXW7β exon usage in patients with B-ALL. (A) FBXW7β exon usage correlated with LTB, LST1, CD52, and MME transcript expression in primary B-ALL patient samples from St. Jude Children’s Hospital. (B) Top: STRING association network indicating functional association of LTB with members in the TNF superfamily signaling pathway. Bottom: STRING association network illustrating co-expression (black lines) of LST1 with other genes. (C) Schematic of HLA genomic loci. Within the HLA Class III region, a gene cluster containing TNF is involved in inflammation. (D) Transcript expression of several members in the TNF superfamily signaling pathway correlated with FBXW7β exon usage in patients with B-ALL from St. Jude Children’s Hospital. Among those that exhibit positive correlation in (C) and (D), LTB, LST1, NCR3, LTA, and NFKBIL1 gene loci are clustered in the same TNF genomic region. (E) Correlations between transcript expression of ∼40 000 genes and the FBXW7β exon usage. Genes were ranked by the Spearman correlation coefficients (rho values). Positive rho values indicate positive correlations. Near-zero rho values indicate lack of correlation.