Figure 4. Optical principle for axially sweeping of a light-sheet.
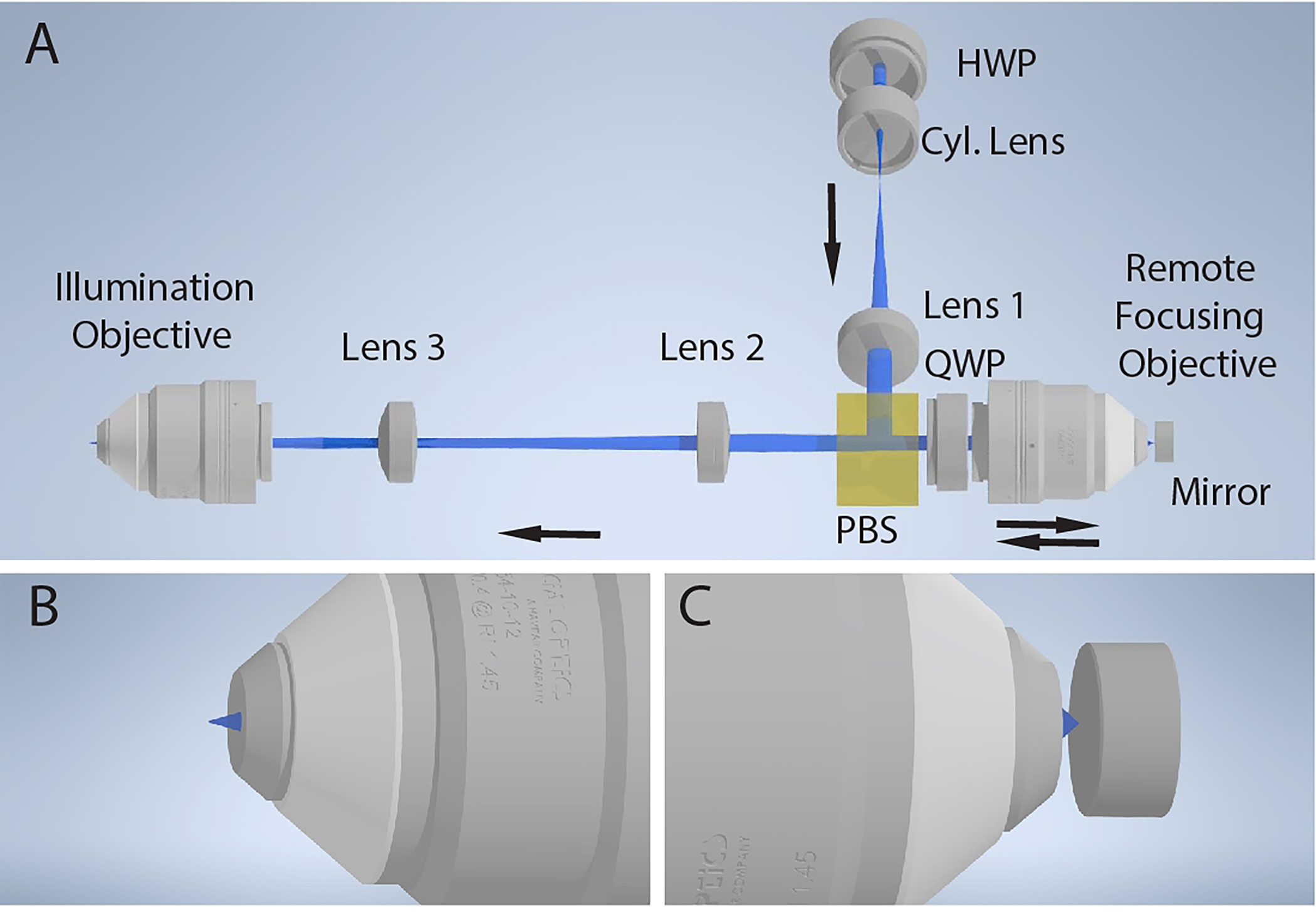
a, Basic schematic of the remote focusing system for axial scanning of the light-sheet. A 1-dimensional light-sheet is created with a cylindrical lens (Cyl. Lens), recollimated with an achromatic doublet (Lens 1), reflected with a polarizing beam splitter (PBS), and focused onto a mirror with a remote focusing objective. The light is back reflected, passed through the polarizing beam splitter, relayed with a pair of achromatic doublets (Lenses 2 and 3), and focused into the specimen with an illumination objective. The half-wave plate (HWP) is rotated to maximize reflection of the light off the polarizing beam splitter, and the rotation of the quarter-wave plate (QWP) is rotated to maximize transmission through the polarizing beam splitter on the reverse path. b, Diffraction-limited light-sheet at the focus of the illumination objective. c, Laser focused onto the mirror by the remote focusing objective. An axial translation of the mirror results in an axial shift in the position of the diffraction-limited light-sheet at the focus of the illumination objective.
