Fig. 1.
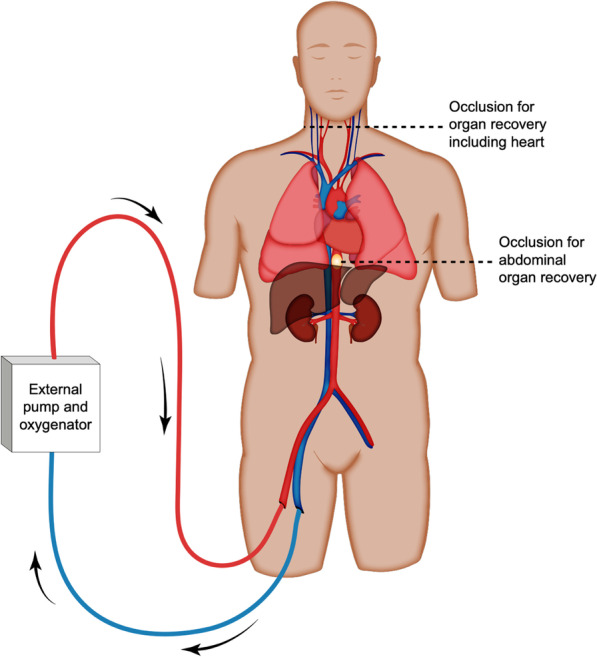
Use of ECMO circuit in eCPR, NRP for cDCD, and NRP for uDCD. ECMO extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; eCPR extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation; NRP normothermic regional perfusion; cDCD controlled donation after circulatory death; uDCD uncontrolled donation after circulatory death. The ECMO circuit consists of a venous access cannula, draining venous blood to a pump device, which pumps deoxygenated venous blood through an oxygenator membrane that also scavenges carbon dioxide and manages temperature. The oxygenated blood returns to a central artery via an arterial return cannula. In eCPR, the goal is to achieve return of spontaneous circulation with good neurological function. Critical to achieving that goal is providing circulation of oxygenated blood to the brain. In NRP, balloon occlusion in the aorta at the level of the diaphragm (to recover abdominal organs) or surgical ligation of blood vessels to the brain (to recover the heart) is performed to ensure natural progression of complete and irreversible loss of brain function postmortem
