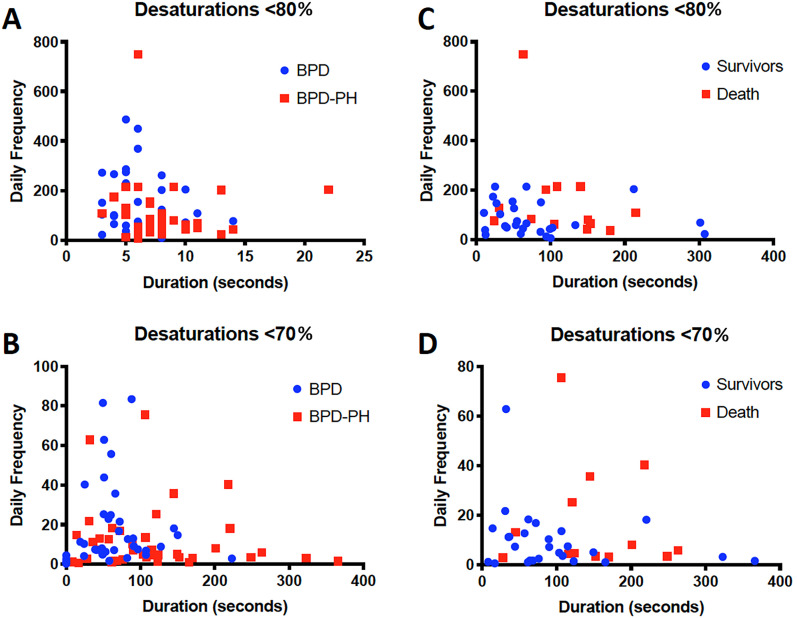
Figure 2.
Intermittent hypoxemic events by pulmonary hypertension (PH) and survival. (A and B) Characterization of intermittent hypoxemic events in the week preceding the initial echocardiographic diagnosis of bronchopulmonary dysplasia associated PH (BPD-PH; n = 40) compared with events in infants with BPD without PH (n = 40). (C and D) Comparisons within infants with BPD-PH between survivors (n = 27) and infants that died (n = 13). Events are stratified by thresholds of intermittent hypoxemia events ([A and C] <80%; [B and D] <70%) with further classification by median frequency and median duration of observed events. Data using a threshold below 70% are not exclusive to data using a threshold below 80%. The duration of events differed between cases and control subjects for desaturations (<80%: P = 0.03; <70%: P = 0.008) and between survivors and infants that died with events less than 70% (P = 0.01). The frequency of events did not differ.