FIG 3.
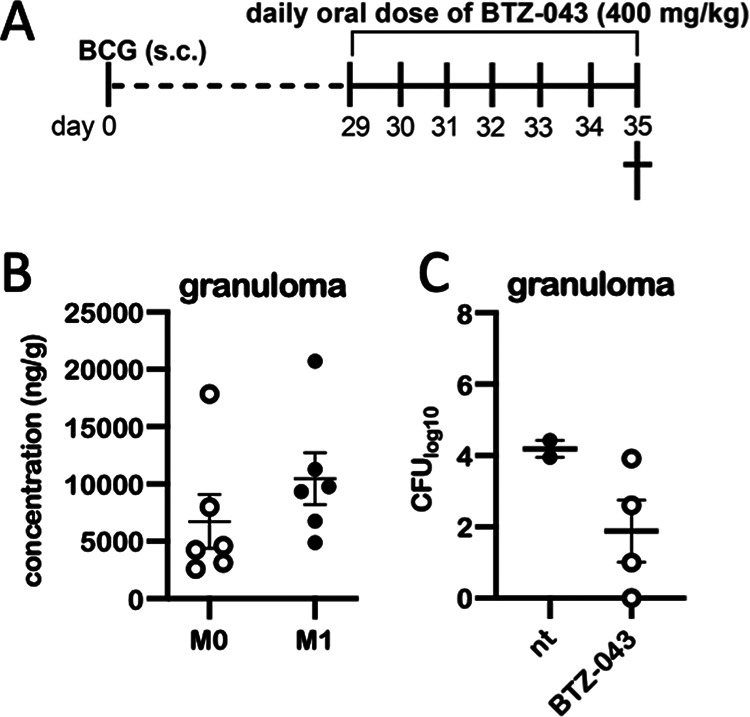
High levels of BTZ-043 are reached in BCG-induced granulomas. (A) Six guinea pigs were inoculated subcutaneously with 1 × 106 CFU of BCG Pasteur 1173. After 28 days, treatment with a daily oral dose of 400 mg/kg of BTZ-043 was started and continued for 7 consecutive days. At day 35, guinea pigs were euthanized and BCG-induced granulomas at the injection site were taken for analysis. (B) Parts of granulomas were cryopreserved and levels of BTZ-043 (M0) and its metabolite (M1) were measured via mass spectrometry. Individual levels and the means of M0 and M1 are shown for each of the six animals. Error bars represent the standard errors of the means. (C) For four treated animals, parts of granulomas were homogenized, serially diluted, and plated on 7H11 agar plates. After 3 weeks, CFU were counted. Results from two additional guinea pigs that were inoculated with BCG but not treated (nt) are depicted for comparison.
