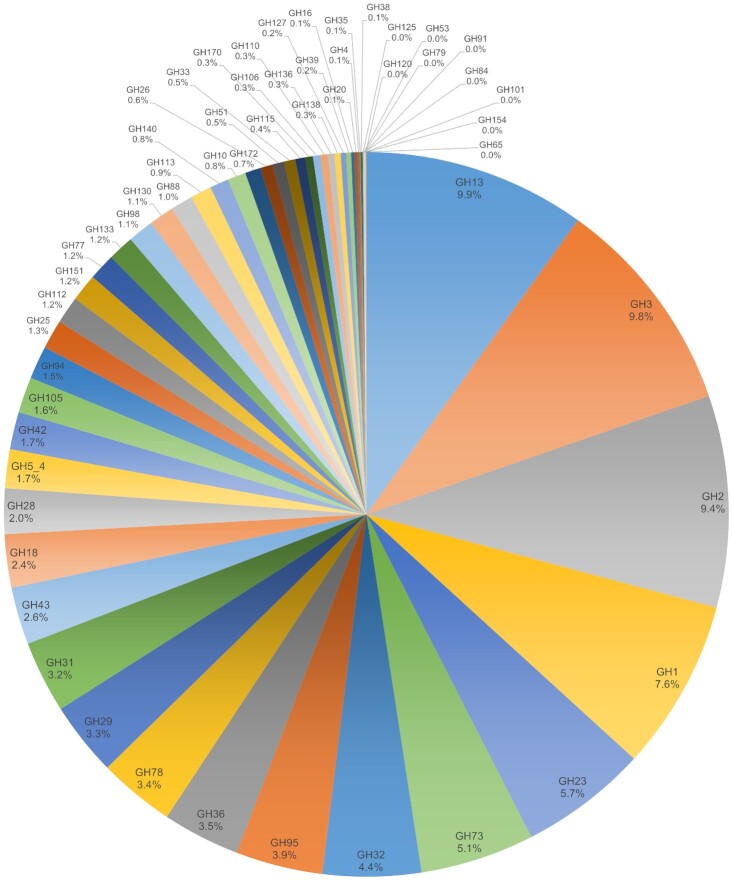
Figure 2.
Distribution of GHs across R. gnavus strains. A total of 7741 putative GHs has been identified by analysing 92 genomes of R. gnavus strains. These GHs are spread across 56 GH families. Some GH families are not widely spread amongst R. gnavus strains (i.e. GH35, GH38, GH53, GH65, GH79, GH84, GH91, GH101, GH120, GH125, and GH154) while other families are present in all the strains (i.e. GH1, GH2, GH3, GH13, GH18, GH25, GH29, GH31, GH32, GH36, GH73, GH77, GH78, GH95, GH112, and GH151). More than half of the sequences (4021/7741) belongs to seven GH families: GH1, GH2, GH3, GH13, GH23, GH32, and GH73. Combined, these families cover enzymes with a wide range of activities including (but not exclusively) α-amylase, isoamylase, pullulanase, β-glucosidase, β-galactosidase, β-mannosidase, β-glucuronidase, β-xylosidase, lysozyme, peptidoglycan hydrolase, invertase, inulinase, and endo-levanase.