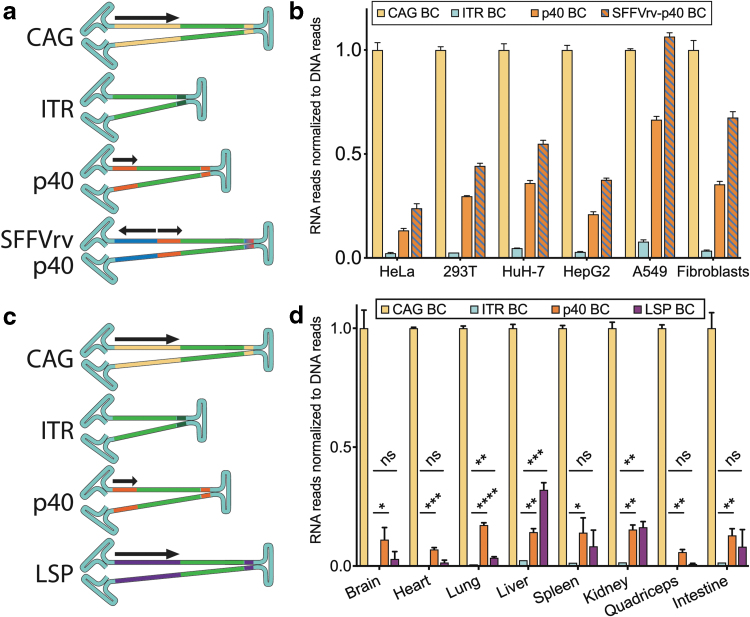
Figure 4.
Rep2-p40 activity in vitro and in vivo. (a, b) Uniquely barcoded scAAV constructs used in the study shown in (b). Arrows indicate the direction in which the promoters are orientated. EXI based on Illumina sequencing of RNA and DNA purified from cells transduced with AAV-7m8 encoding barcoded scAAV-“Promoter”-GFP constructs from (a). To obtain EXI, the RNA/cDNA signal was adjusted to the entry of each construct (DNA reads). The final EXI was subsequently normalized to scAAV-CAG-GFP, which was assigned a value = 1. MOT = 500 and 5,000 vector genome per cell, N = 1 for each MOT for all cell types, values shown are averages of both MOTs. (c, d) Uniquely barcoded constructs (d) packaged into scAAV9 were used to transduce mouse in vivo. Illumina sequencing was used to analyze vector entry (DNA) and expression (RNA) in indicated tissues, and results were used to calculate an EXI. The final EXI was subsequently normalized to scAAV-CAG-GFP, which was assigned a value = 1. Total vector dose = 1 × 1011 vector genome copies per mouse, intravenous injection, N = 3 for all tissues. Statistics: Nonparametric multiple comparison's t-test (Holm–Sidak) compared with ITR indicated as asterisk for adjusted p-values: 0.05 > * ≥ 0.01 > ** ≥0.001 > *** ≥0.0001 > ****. CAG, cytomegalovirus enhancer–chicken β-actin promoter–globin intron; ITR, inverted terminal repeat; LSP, liver-specific promoter (apolipoprotein E enhancer/human alpha antitrypsin promoter); MOT, multiplicity of transduction; p40, Rep2-p40 promoter.