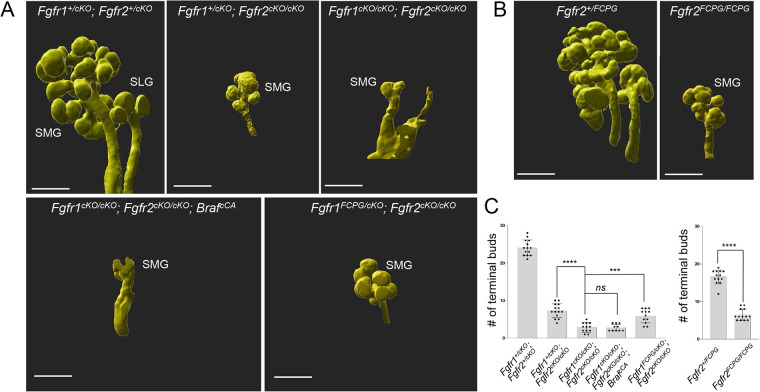
Fig. 3.
Branching in signaling mutants. (A) Whole-mount E-cadherin immunofluorescence followed by 3D rendering was used to analyze changes in the number of terminal buds at E14.5 across various Fgfr1/2 signaling mutants. Fgfr1cKO/cKO; Fgfr2cKO/cKO; BrafCA mutants (n=11) did not rescue branching defects in the submandibular gland (SMG). The sublingual gland (SLG) did not develop in these mutants. Compared with severe branching defects observed in Fgfr1cKO/cKO; Fgfr2cKO/cKO mutants (n=17), Fgfr1FCPG/cKO; Fgfr2cKO/cKO mutants (n=12) exhibited a partial rescue of branching defects in the SMG. The SLG did not develop in Fgfr1FCPG/cKO; Fgfr2cKO/cKO mutants. A representative image is shown for each genotype. Scale bars: 200 µm. (B) 3D rendering was used to analyze SMG defects in Fgfr2+/FCPG and Fgfr2FCPG/FCPG mutants at E14.5. Fgfr2FCPG/FCPG mutants (n=13) did not develop SLGs and showed reduced terminal bud numbers in the SMG. Scale bars: 200 µm. (C) The mean terminal bud number (±s.d.) in the SMG for various Fgfr1 and Fgfr2 signaling mutants at E14.5 are represented in bar graphs. Fgfr1cKO/cKO; Fgfr2cKO/cKO mutants (n=17) showed a 94.5% reduction in terminal bud numbers. A similar level of reduction was observed upon ectopic activation of BRAF in Fgfr1cKO/cKO; Fgfr2cKO/cKO; BrafcCA mutants (n=11). Fgfr1FCPG/cKO; Fgfr2cKO/cKO mutants (n=12) rescued branching defects by 19.1%. A 61% reduction in terminal bud number was observed in Fgfr2FCPG/FCPG mutants (n=12) compared with controls. Data are mean (±s.d.), ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001; ns, P<0.05 (one-way ANOVA using Bonferroni multiple comparisons test, two tailed, or a two-tailed Student's t-test).