Figure 18.
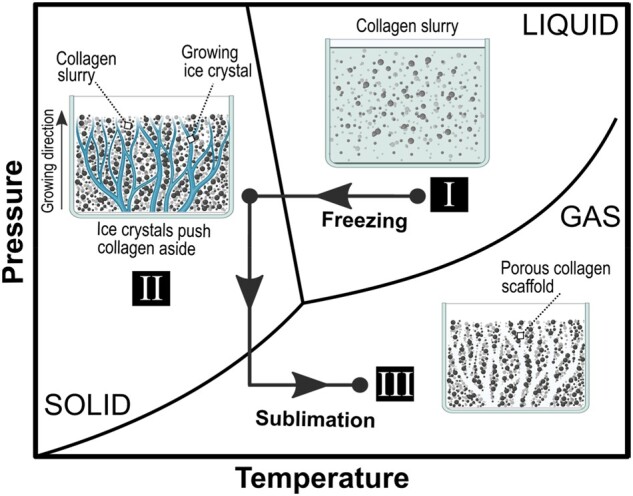
Phase diagram showing the ice solidification process and formation of a porous scaffold by means of freeze-drying. This process commences with the gradual cooling of a water-based polymer/ceramic suspension or solution below its equilibrium freezing temperature (I). the growing ice crystals exclude the polymer or ceramic dissolved as dispersed in the mould, due to the ‘self-cleaning’ nature of ice, resulting in a stable dendritic ice crystal morphology (II). the subsequent sublimation step is induced by changing the pressure and temperature of the freeze-dryer, resulting in a porous scaffold with the polymer occupying positions defined by the ice crystal boundaries (III).
