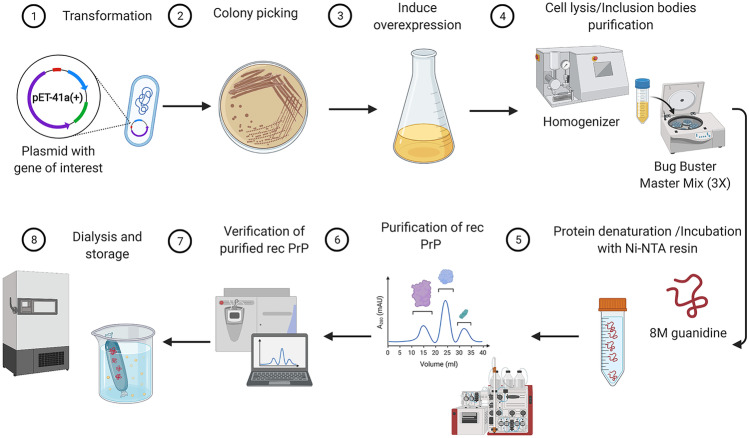
Fig. 1.
Overview on different steps of rec PrP production and purification. The first step in protein purification is the insertion of the vector (e.g., pET-41a( +)) into competent E. coli bacteria via heat shock transformation (1). The transformed bacteria are plated on LB agar plates with selective antibiotics (2). Due to the vector-induced antibiotic resistance, only bacteria with vector will grow (2). A single colony is picked from the agar plates and incubated in LB medium for overexpression by IPTG induction or overnight in auto-induction medium (3). Subsequently, bacteria will be centrifuged, the pellet will be weighted, and the BugBuster Master mix or lysis buffer will be added according to the pellet weight followed by homogenization and centrifugation (4). Once the inclusion bodies are purified, the pellet becomes denatured and incubated with Ni–NTA beads (5). After column is attached to ÄKTA pure micro system, rec PrP becomes refolded and eluted (6). The purified rec PrP is collected from the elution step and verified either by Western blotting, Coomassie staining, and/or mass spectrometry (7). The last step in protein purification is the dialysis of the purified rec PrP followed by storage at − 80 °C (8) (created by BioRender)