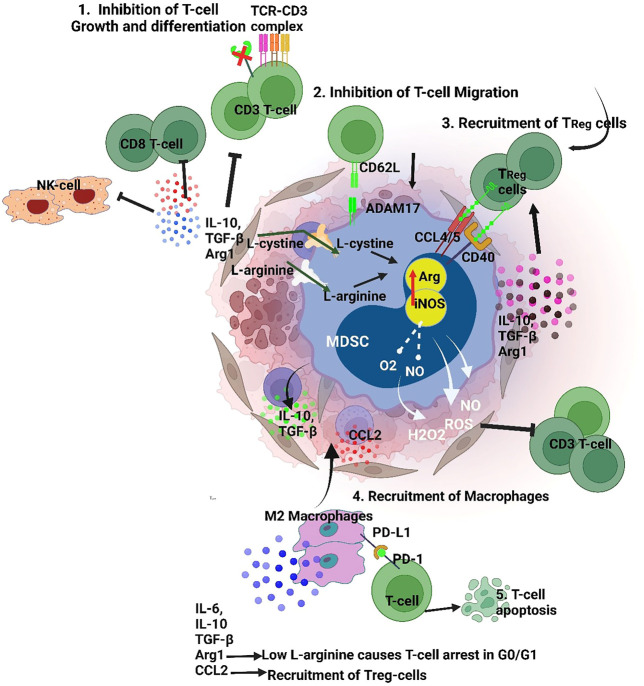
FIGURE 1.
MDSCs suppressive mechanism targets both innate and adaptive immunity 1. Targeting T cell and NK cell function by TGFβ/IL10 induced inhibition. Also, MDSCs release ROS, H2O2 and peroxynitrite which dysregulate the TCR Z chain inhibiting T-cell/MDSC interaction 2. MDSCs maintain a pre-metastatic niche inhibiting T-cell migration, 3. MDSCs interact with Tregs via CCL4/5 and CD40 that recruitments them to the TME, 4. MDSCs induce a M2 macrophage phenotype by secretion of IL-10, thereby promoting immune escape for tumor cells. Furthermore, secretion of factors like IL-10 and TGF-b, and reduction of L-arginine by MDSCs induce Treg polarization. (iNOS-Inducible nitric oxide synthase, Arg- Arginase, PD-L1- Programmed death-ligand 1, TGFβ- Transforming growth factor beta, IL-10- Interleukin 10, 1L-6- Interleukin 6,CCL-2- C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2, CCL4- C-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 2, ADAM17-a disintegrin and metalloprotease domain).