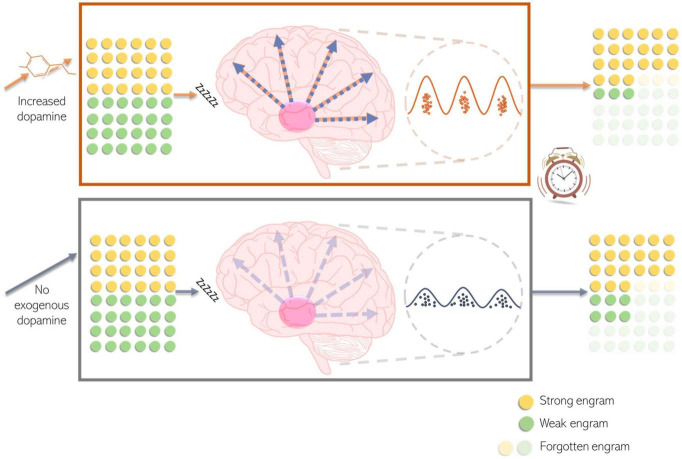
FIGURE 8.
Model of dopamine modulation of memory. Some routine information forms a stronger (yellow) memory engram than other routine information (green), for example due to re-exposure or salience. While capacity for overall consolidation remains the same, an increase in dopamine availability causes destabilisation and preferential forgetting of weak engrams. Dopamine modulates this memory selection by enhancing synchronisation in cortical firing patterns during spindles, at the peak of slow-waves. Together these two processes (enhanced forgetting and cortical synchronisation) bias subsequent memory.