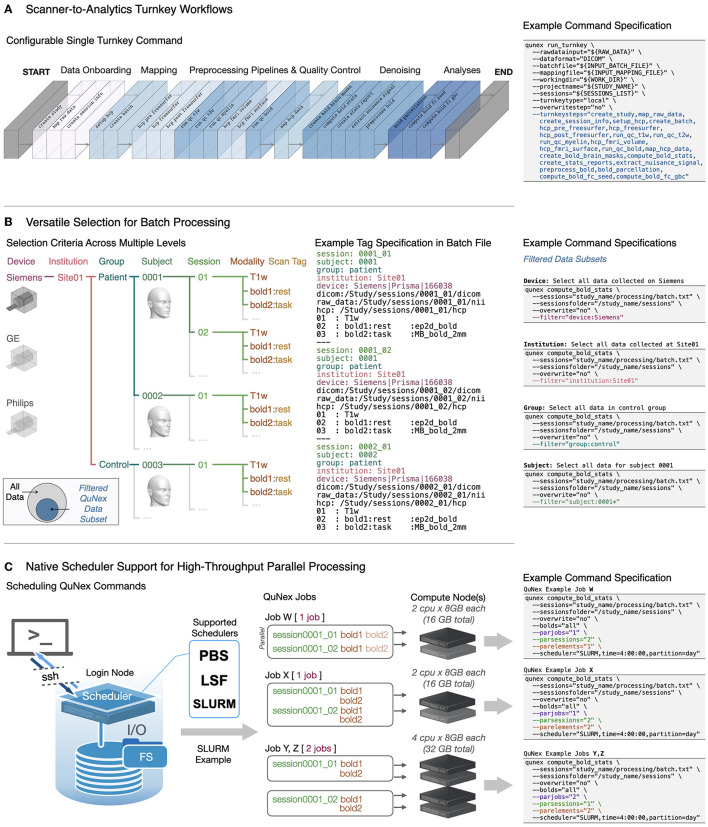
Figure 2.
QuNex turnkey functionality and batch engine for high-throughput processing. (A) QuNex provides a “turnkey” engine which enables fully automated deployment of entire pipelines on neuroimaging data via a single command (qunex run_turnkey). An example of a typical workflow with key steps supported by the turnkey engine is highlighted, along with the example command specification. QuNex supports state-of-the-art preprocessing tools from the neuroimaging community (e.g., the HCP MPP; Glasser et al., 2013). For a detailed visual schematic of QuNex steps and commands (see Supplementary Figure 1). (B) The QuNex batch specification is designed to enable flexible and comprehensive “filtering” and selection of specific data subsets to process. The filtering criteria can be specified at multiple levels, such as devices (e.g., Siemens, GE, or Philips MRI scanners), institutions (e.g., scanning sites), groups (e.g., patient vs. controls), subjects, sessions (e.g., time points in a longitudinal study), modalities (e.g., T1w, T2w, BOLD, diffusion), or scan tags (e.g., name of scan). (C) QuNex natively supports job scheduling via LSF, SLURM, or PBS schedulers and can be easily deployed in HPC systems to handle high-throughput, parallel processing of large neuroimaging datasets. The scheduling options enable precise specification of paralellization both across sessions and within session (e.g., parallel processing of BOLD images) for optimal performance and utilization of cluster resources.