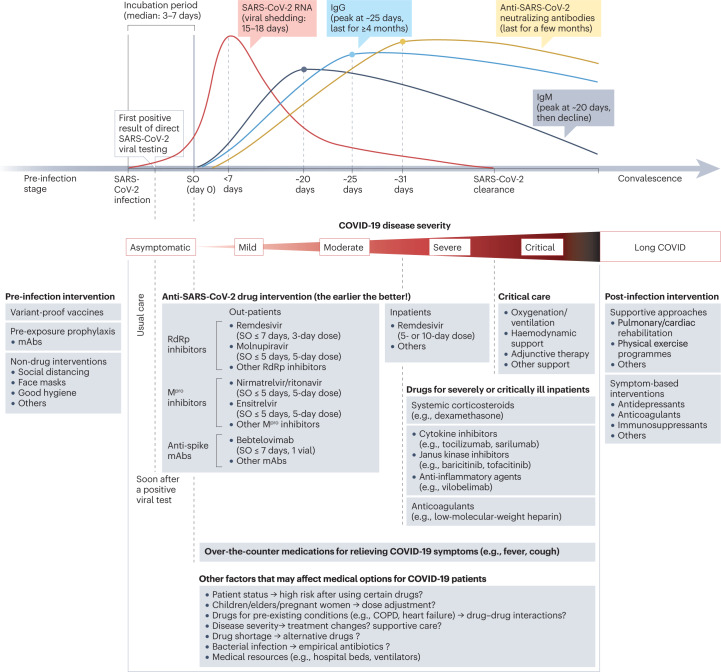
Fig. 8. Therapeutic strategies for COVID-19 and future coronavirus outbreaks.
a, Therapeutic interventions at various stages of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). At the pre-infection stage, variant-proof vaccines, pre-exposure prophylaxis and nonpharmaceutical interventions can be considered. Once severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection is diagnosed, anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapies are ideally administered to outpatients as soon as possible so that the viral load is significantly reduced at an early stage. SARS-CoV-2 viral load usually peaks within the first week after symptom onset (SO) and SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding in the upper respiratory tract has a mean duration of approximately 17 days287. Levels of anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin M (IgM), IgG and neutralizing antibodies peak at approximately 20, 25 and 31 days, respectively288. At the advanced stage of COVID-19 progression, immunomodulators, anticoagulants, anti-inflammatory drugs and/or critical care can be considered for severely or critically ill inpatients under certain conditions (Box 1). Post-infection interventions might be needed for some survivors experiencing persistent symptoms after COVID-19 infection289. COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; mAbs, monoclonal antibodies; Mpro, main protease; RdRp, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase.