FIGURE 4.
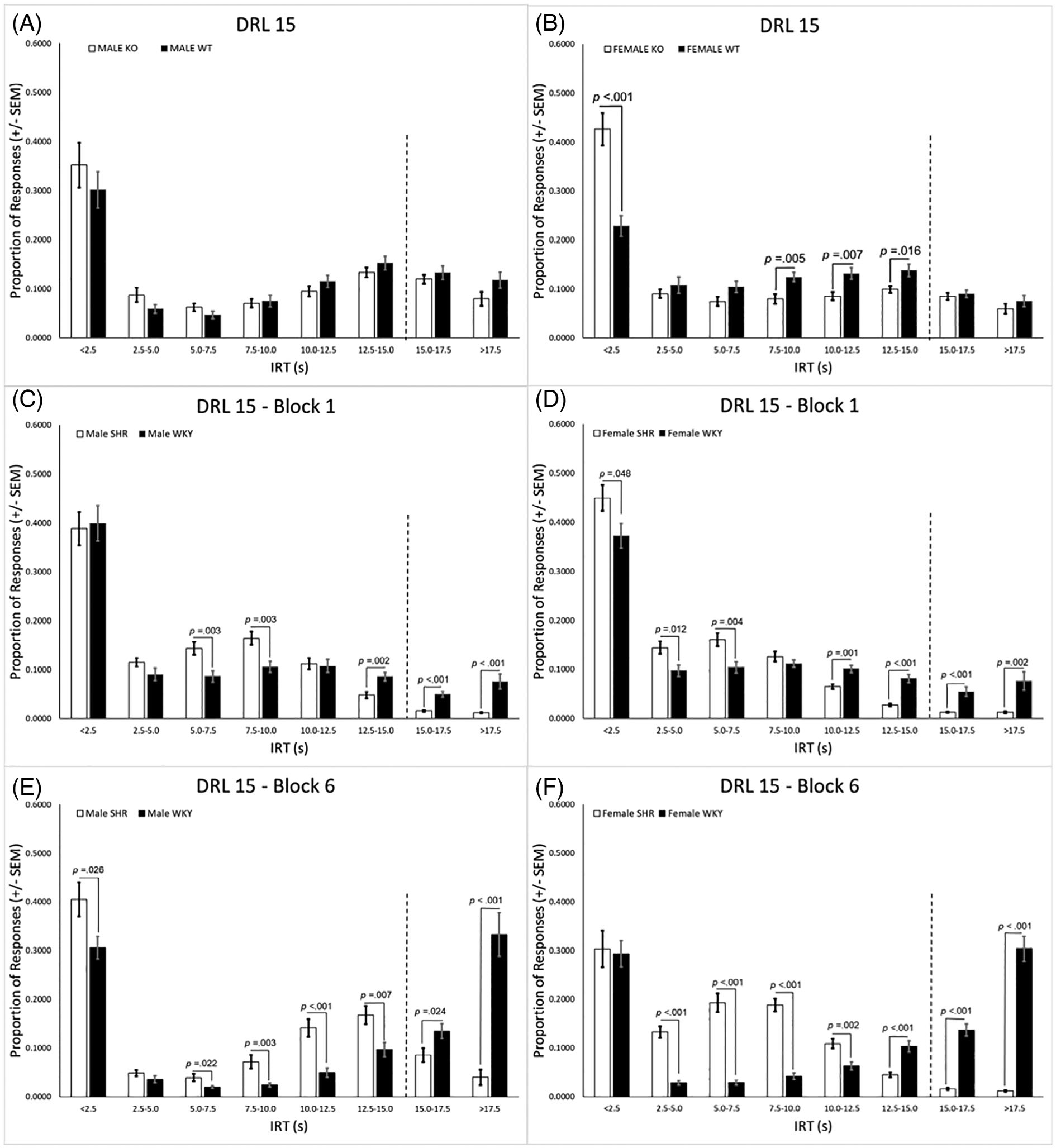
(A) The genotype x IRT interaction was not significant in the males. (B) Compared with WT females, KO females exhibited a significantly higher proportion of burst responses in the shortest IRT bin, but a lower proportion of responses in bins ranging from 7.5–15.0 s. (C) In block 1, SHR males had a higher proportion of responses in intermediate IRT bins ranging from 5.0–10.0 s, but a lower proportion of responses in IRT bins greater than 12.0 s when compared with WKY males. (D) SHR females in block 1 had a significantly higher proportion of responses than WKY females in the IRT bins that were less than 7.5, but a lower proportion of responses in IRT bins greater than 10.0 s. (E) In block 6 the SHR males exhibited a significantly higher proportion of responses than WKY males in all but one of the IRT bins less than 15.0 s, as well as a lower proportion of responses in both bins greater than 15.0 s. (F) SHR females in block 6 exhibited a significantly higher proportion of responses than WKY females in all bins ranging from 2.5–12.5 s, but a significantly lower proportion in the three longest IRT bins. DRL, differential reinforcement of low rates; KO, knockout; SEM, standard error of the mean; SHR, spontaneously hypertensive rat; WKY, Wistar-Kyoto; WT, wildtype
