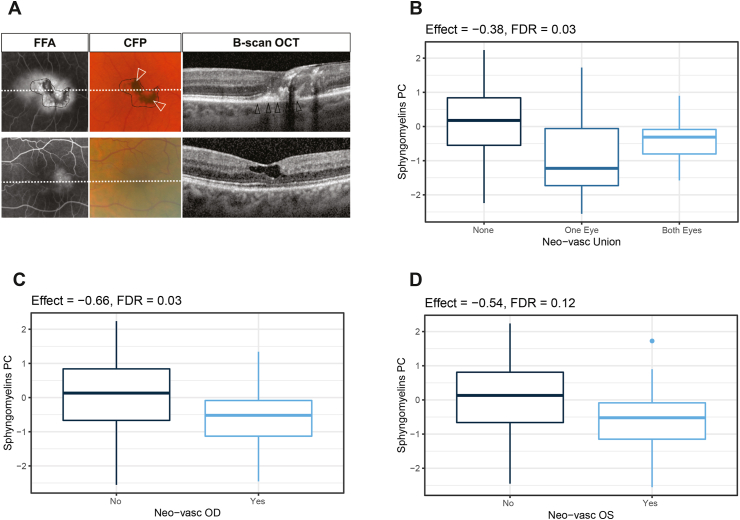
Figure 3.
MacTel patients presenting neovascularization have reduced levels of sphingomyelins. (A) Representative left eyes of two MacTel patients with low (top) and high (bottom) sphingomyelin serum levels. Eye with a large subretinal/sub-RPE neovascular membrane (black arrowheads) and pigment accumulation (white arrowheads) (top) and eye with mild parafoveal leakage on fundus fluorescein angiography (FFA) and lack of hyper-reflective changes on OCT (bottom). (B) Association between sphingomyelins principal component score and neovascularization in both eyes (left + right). Center line indicates the median and box boundaries denote the 25th and 75th percentiles. (C) Association between sphingomyelins principal component score and neovascularization in right eyes (OD) only. Center line indicates the median and box boundaries denote the 25th and 75th percentiles. (D) Association between sphingomyelins principal component score and neovascularization in left eyes (OS) only. Center line indicates the median and box boundaries denote the 25th and 75th percentiles.