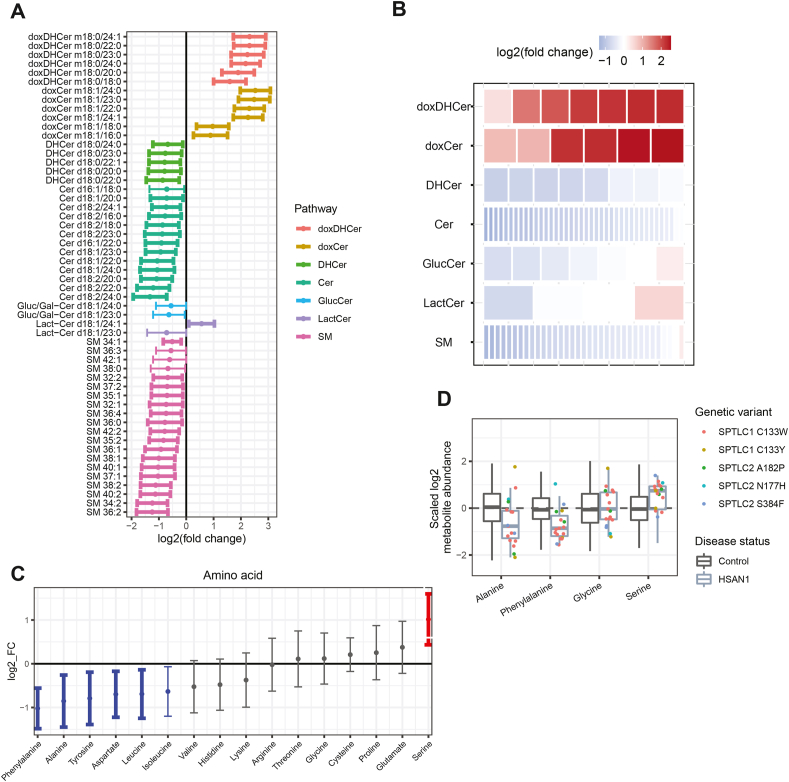
Figure 4.
HSAN1 patients have altered circulating levels of canonical ceramides and amino acids. (A) Representation of all significantly different SL species (p < 0.05) comparing HSAN1 to Controls. Color indicates the lipid class and bold bars indicate significance after correction for FDR. (B) Changes in abundance across SL classes. Each row is composed of tiles representing lipids contained in the group. The color of each tile represents the mean log fold change of that lipid in HSAN1 patients to Controls. The color blue represents depletion and red represents increased abundance. (C) Change in 16 amino acids comparing HSAN1 to Controls. Points indicate mean log fold change and bars extend to the 95% confidence interval of the mean. Red or blue colors indicate nominal significance (p < 0.05), and bold bars indicate significance after correction for FDR. (D) Distribution of alanine, phenylalanine, glycine, and serine levels in HSAN1 subjects (excluding those on serine supplementation) compared to Controls. HSAN1 subject metabolite abundance (points) are colored according to genetic variant. Individual data points for Controls are not shown. Boxplot central line indicates the median and box boundaries denote the 25th and 75th percentiles. Whiskers extend to the most extreme values within 1.5× the interquartile range. Abbreviations: doxDHCer, deoxydihydroceramide; doxCer, deoxyceramide; DHCer, dihydroceramide; Cer, ceramide; Gluc/Gal-Cer or GlucCer, glucosyl/galactosyl-ceramide; Lact-Cer, lactosyl-ceramide; SM, sphingomyelin; SPTLC1 and SPTLC2, serine-palmitoyl transferase long chain subunit 1 or 2.