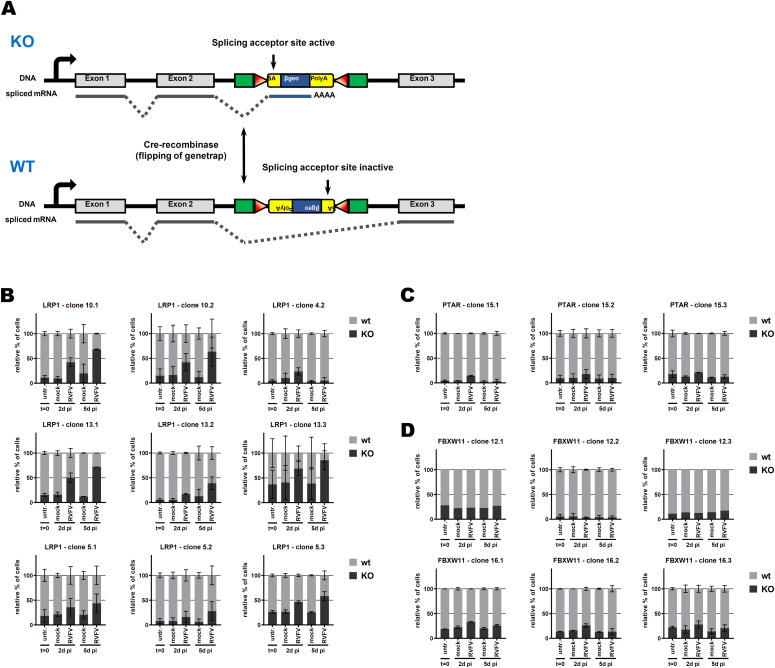
Figure 2. Growth competition assay in mouse embryonic stem cells.
(A) Schematic representation of the genetrap system when inserted into an intron. When in sense orientation, the genetrap exposes a splicing acceptor site and will be inserted into the mature mRNA, leading to a knockout of the gene of interest. When in antisense orientation, the splicing acceptor site is inactive and the genetrap will be spliced out, leading to a WT expression of the gene of interest. Flipping of the genetrap orientation is possible by expressing the Cre recombinase. (B, C, D) Growth competition assay between sister clones bearing a genetrap into the gene of interest ((B): LRP1, (C): PTAR, and (D): FBXW11). Sister clones with WT phenotype are in grey, and sister clones with knockout phenotype are in black (see Table 1). ∼30% of knockout cells were mixed with 70% of their WT sister clone, and infected with RVFV MP-12 at an MOI of 5. The ratio between both sister clones was followed by flow cytometry. n = 2, except if the event count was below 1,000, in which case the whole data set was removed (n = 1).