Figure 7.
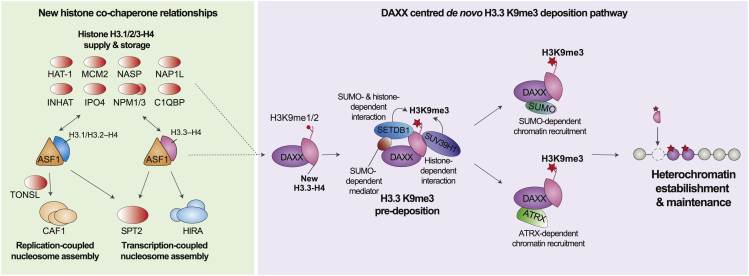
DAXX adds a de novo H3.3K9me3 deposition pathway to the histone chaperone network
During histone supply ASF1 handles H3.1/2/3–H4 dimers and forms several histone-dependent co-chaperone complexes with other histone chaperones, notably ASF1 channels H3 variants toward distinct deposition complexes on chromatin. We identified a new ASF1-centered histone supply pathway to SPT2 that is H3 variant independent, as well as an upstream role for ASF1 in delivering H3.3 histones to DAXX, and an H3.1 variant specificity in TONSL. We found DAXX facilitates the catalysis of H3.3K9me3 through SETDB1 and SUV39H1 methyltransferase recruitment prior to histone deposition on chromatin. DAXX-bound H3.3–H4 recruits SETDB1 and SUV39H1, and the interaction of DAXX with SETDB1 is additionally dependent on SUMOylation. Other factors involved in heterochromatin establishment are differentially dependent on ATRX (e.g., the ChAHP complex) and SUMOylation (e.g., SMCHD1-LRIF1), and we speculate that this represents alternative pathways for H3K9me3 deposition supporting de novo heterochromatin silencing at distinct genomic locations.