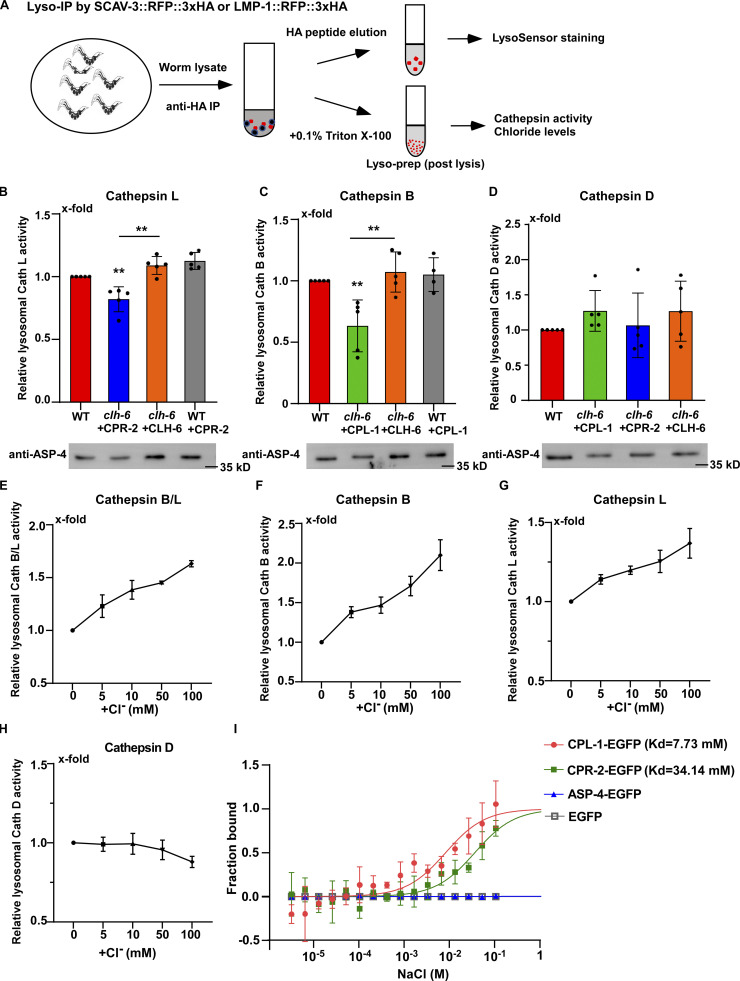
Figure 8.
Loss of clh-6 affects lysosomal cathepsin B and L activity. (A) Schematic illustration of the lysosome purification experiment by LysoIP. (B–D) Relative activity of cathepsin L (B), cathepsin B (C), and cathepsin D (D) in purified lysosomes from the indicated strains. The amount of lysosomes in each strain was determined by Western blot with an anti-ASP-4 antibody. Relative cathepsin activity was quantified as described in the Materials and methods and normalized to onefold in wild type. At least five independent experiments were performed. Data are shown as mean ± SD. Student’s two-tailed unpaired t test was performed to compare mutant datasets with wild type or datasets linked by lines. **P < 0.001, all other points had P > 0.5. (E–H) Chloride supplements increase the activity of cathepsin B and L, but not cathepsin D, in lysosomes purified from wild-type worms. Relative cathepsin activity was quantified as described in the Materials and methods and normalized to onefold in the sample without NaCl addition. NaCl provides Cl− and Na-gluconate was used to substitute Na+ and Cl− in the low NaCl solutions. At least three independent experiments were performed. Data are shown as mean ± SD. (I) Chloride binds to recombinant CPL-1-EGFP and CPR-2-EGFP, but not ASP-4-EGFP or EGFP, in MST assays. At least three independent experiments were performed. Data are shown as mean ± SD. Source data are available for this figure: SourceData F8.