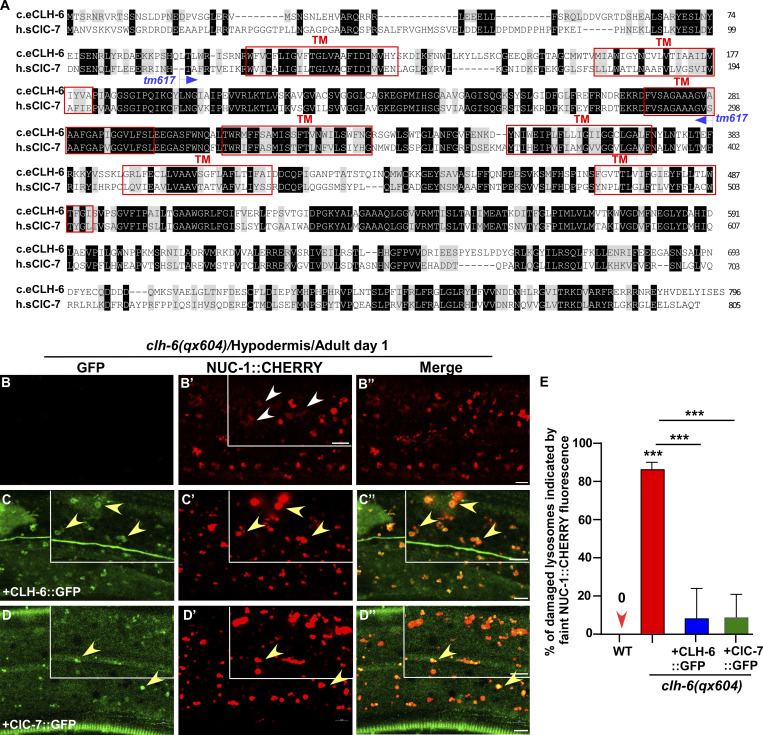
Figure S2.
CLH-6 is homologous to human ClC-7. (A) Sequence alignment of C. elegans (c.e) CLH-6 and human (h.s) ClC-7. Identical residues are shaded in black and similar ones in gray. Red boxes indicate the transmembrane (TM) domains in CLH-6 predicted by uniProt. The region deleted in the tm617 allele is indicated. (B–D′′) Confocal fluorescence images of the hypodermis in clh-6(qx604) mutants carrying NUC-1::CHERRY without (B–B′′) or with expression of CLH-6::GFP (C–C′′) or ClC-7::GFP (D–D′′). Both CLH-6::GFP and ClC-7::GFP colocalize with NUC-1::CHERRY (yellow arrowheads). (E) The percentage of damaged lysosomes indicated by faint NUC-1::CHERRY fluorescence (white arrowheads) is quantified in E. Unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test was performed to compare mutant datasets with wild type or datasets that are linked by lines. At least 10 animals were scored in each strain and data are shown as mean ± SD. ***P < 0.0001. All other points had P > 0.5. Scale bars: 5 µm.