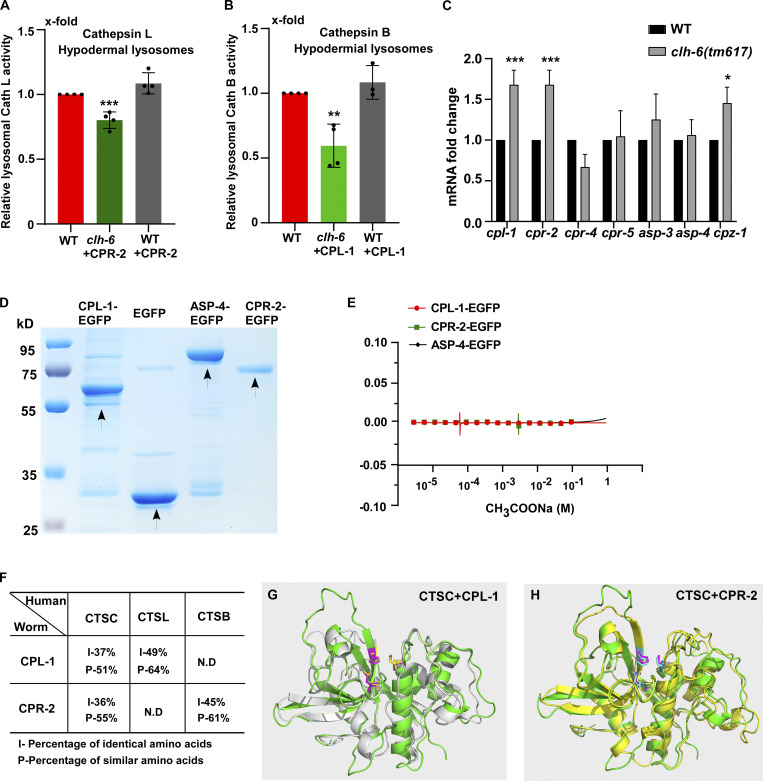
Figure S5.
CPL-1 and CPR-2 share sequence and structural similarity with human cathepsin C. (A and B) Relative activity of cathepsin L (A) and cathepsin B (B) in lysosomes purified from hypodermal cells in the indicated strains. The amount of lysosomes in each strain was determined by Western blot with an anti-ASP-4 antibody. Relative cathepsin activity was quantified as described in the Materials and methods and normalized to onefold in wild type. At least four independent experiments were performed. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR analyses of cathepsin genes in wild type and clh-6(tm617) at adult day 1. At least three independent experiments were performed. In A–C, data are shown as mean ± SD. Student’s two-tailed unpaired t test (A and B) or two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-test (C) was performed to compare CPR-2– or CPL-1–overexpression datasets with wild type (A and B) or mutant datasets with wild type (C). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001, ***P < 0.0001; all other points had P > 0.5. (D) Coomassie blue staining of CPL-1-EGFP, CPR-2-EGFP, ASP-4-EGFP, and EGFP purified from insect cells by two-step affinity purification. (E) Recombinant CPL-1-EGFP, CPR-2-EGFP, and ASP-4-EGFP proteins do not bind to CH3COONa in MST assays. At least three independent experiments were performed. (F) CPL-1 and CPR-2, the C. elegans orthologs of cathepsin L (CTSL) and B (CTSB), respectively, also share sequence similarity with human cathepsin C (CTSC). (G and H) Superimposition of the predicated tertiary structures of C. elegans CPL-1 (gray), with human cathepsin C (CTSC, green; G), and C. elegans CPR-2 (yellow) with human CTSC (green; H). The tertiary structures are predicated by AlphaFold. Key active site residues are highlighted in magenta (CTSC), yellow (CPL-1), and blue (CPR-2). Source data are available for this figure: SourceData FS5.