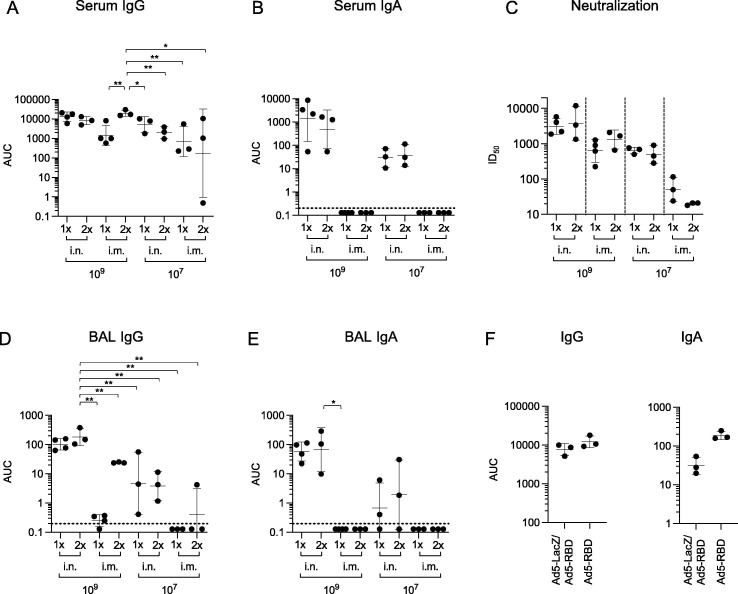
Fig. 3.
Humoral responses to one vs. two treatments with Ad5-RBD administered intranasally (i.n.) or intramuscularly (i.m.) in HLA-DQ6 mice, and lack of effect of pre-treatment with Ad5 vector on priming with Ad5-RBD. Groups of adult male and female mice (n = 3) were inoculated either once or twice (14 days apart) with Ad5-RBD at doses 107 or 109 viral particles/mouse (a-e). Anti-spike IgG or IgA serum antibodies (a, b; area under the curve (AUC)), SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus neutralization (c; calculated serum dilution producing 50% inhibition (ID50)), and anti-spike IgG and IgA bronchoalveolar lavage fluid antibodies (d, e; AUC) were measured after 28 days. In a different experiment, one group of HLA-DQ6 mice was pre-treated i.n. with Ad5-vector encoding β-galactosidase (Ad5-LacZ; 109 vp/mouse), while a second group remained untreated (n = 3; 3f). After 21 days, a priming dose of Ad5-RBD i.n. was administered to both groups (109 vp/mouse). Serum was collected after 42 days, and anti-spike IgG or IgA serum antibodies were measured (f; AUC). For statistical comparisons, one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test for multiple comparisons (a, b, d, e, f) or Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn’s test for multiple comparisons (c) were used. Adjusted p-values are displayed as * <0.05, ** <0.01 and *** <0.001. Lines and bars represent geometric means and standard deviations. Dotted line represents the limit of detection of the assay.