Extended Data Fig. 9 |. DUF616 family sequences are predicted to be a GT-A fold type.
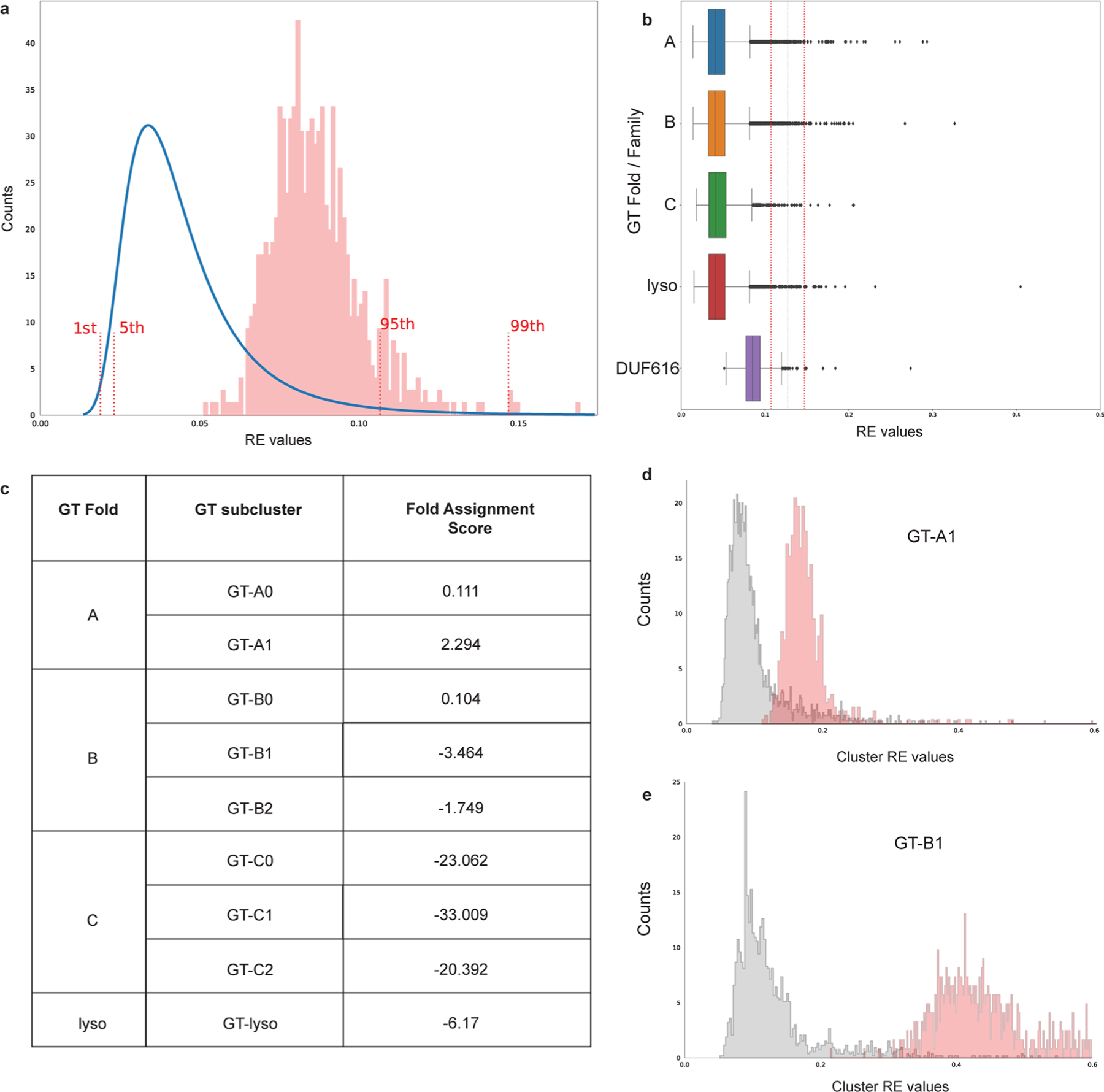
a, Reconstruction error (RE) values are calculated for DUF616 (n = 678) sequences and fall within 95% CI of the RE values for GT-A, B, C and lyso type folds suggesting that DUF616 belongs to one of the known folds. The reference RE values (blue line) were combined from the training set consisting of 39713 GT-A, GT-B, GT-C and GT-lyso sequences. b, RE values for the GT-A (n = 12,316), B (n = 20,397), C (n = 1,518), lyso (n = 5482) and DUF616 (n = 678) sequences are shown as boxplots. Dotted lines mark the 95th and the 99th percentile upper bounds. Boxes show the first and third quartiles. The line within the box indicates the median value. The whiskers mark 1.5 times the interquartile range, excluding the outliers shown as individual diamonds. c, Highest Fold Assignment Scores are found to be for the GT-A1 subcluster for the DUF616 sequences, suggesting that the sequences from this novel family adopt a GT-A type fold. d and e, The RE values against sub cluster GT-A1 and GT-B1 are plotted for DUF616 sequences. As seen, the RE values for GT-A1 are much closer to the true RE values, suggesting overall similarity in core structural fold.
