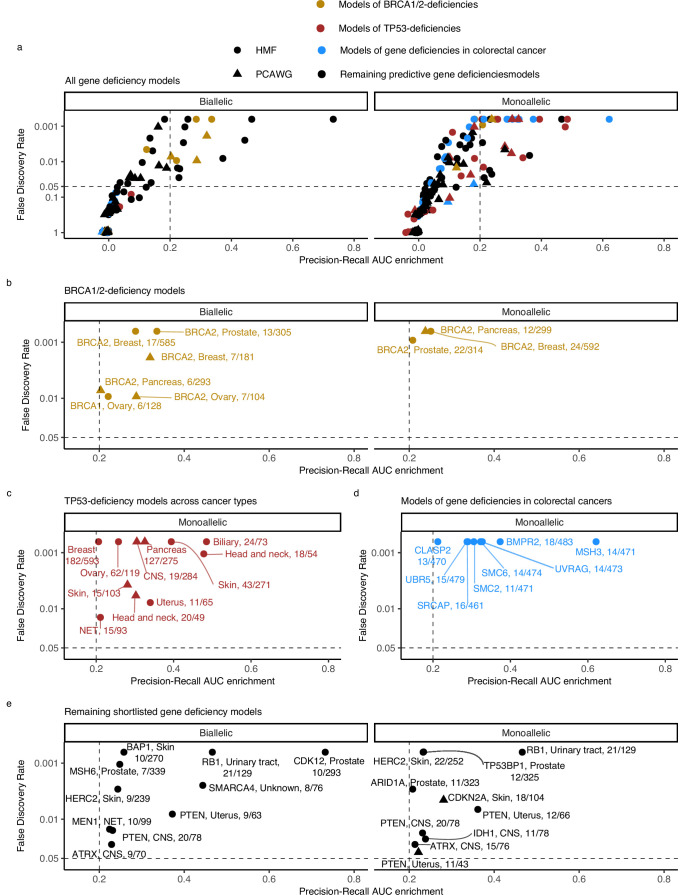
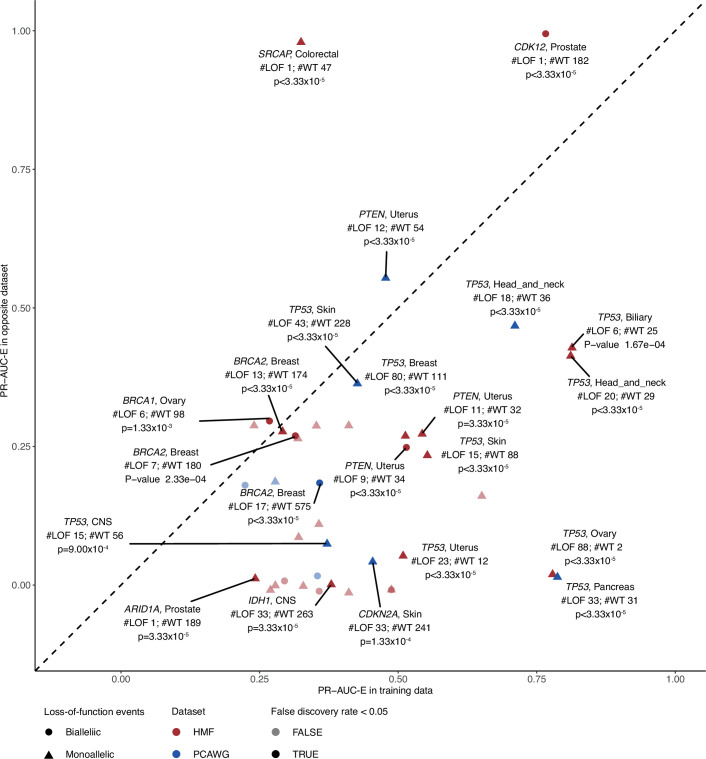
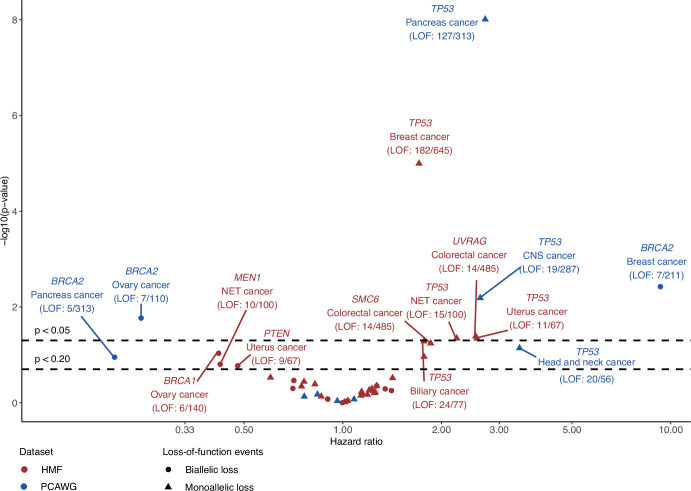
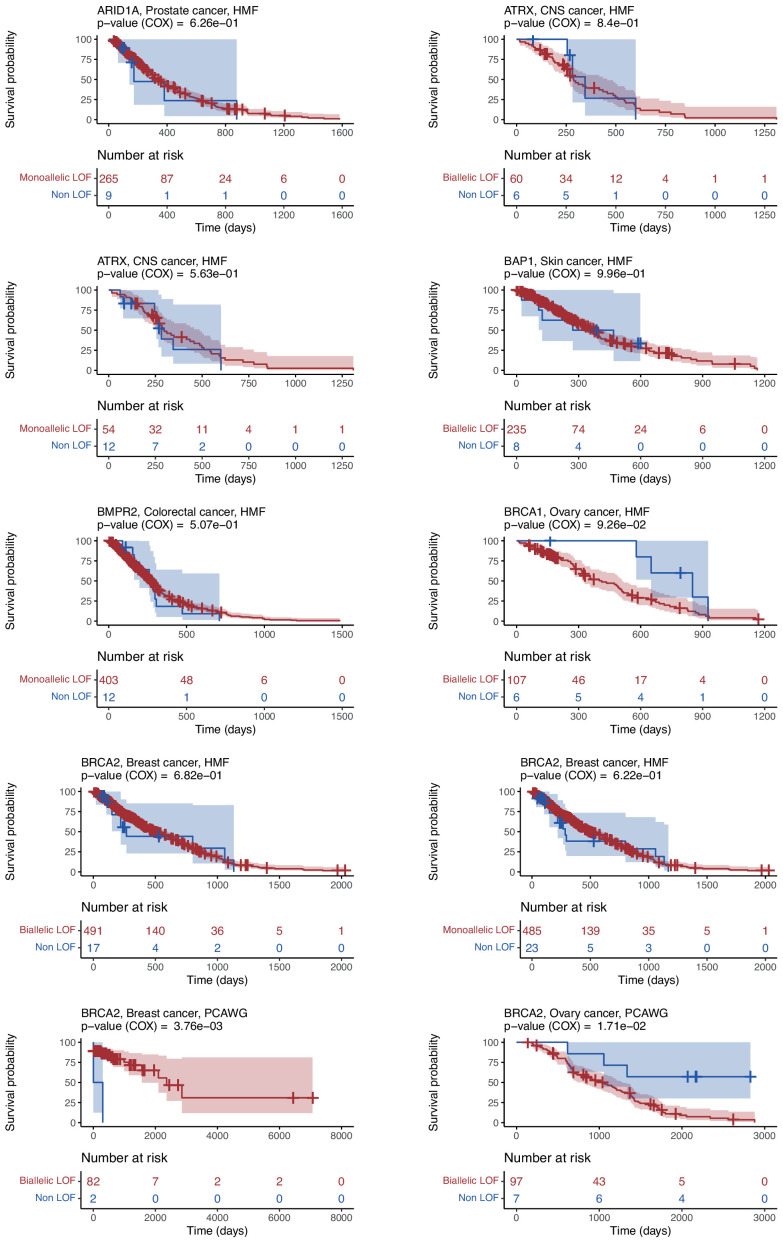
Figure 3. Predictive models of DNA damage response (DDR) gene deficiencies.
(a) The precision-recall AUC enrichment PR-AUC-E; x-axis and significance (false discovery rate [FDR]; logarithmic y-axis) of the 535 predictive models (one model per gene with more than 5 biallelic or more than 10 tumours either mono- or biallelic mutated in either Hartwig Medical Foundation (HMF) or The Pan-Cancer Analysis of Whole Genomes (PCAWG) in any one cancer type; Methods). Significance (q-value representing FDR) evaluated by counting equally or more-extreme PR-AUC-E values across >10,000 permuted data sets and applying Benjamini–Hochberg FDR control. Models with FDR below 0.05 and PR-AUC-E above 0.2 are shortlisted (Methods). (b) Shortlisted predictive models of deficiency of BRCA1 or BRCA2; (c) TP53 monoallelic predictive models; (d) monoallelic gene deficiency models across colorectal cancer patients; and (e) remaining gene deficiency models not contained in the other sub-groups. Numbers indicate the number of mutated out of the total number of tumours included in the development of each model.