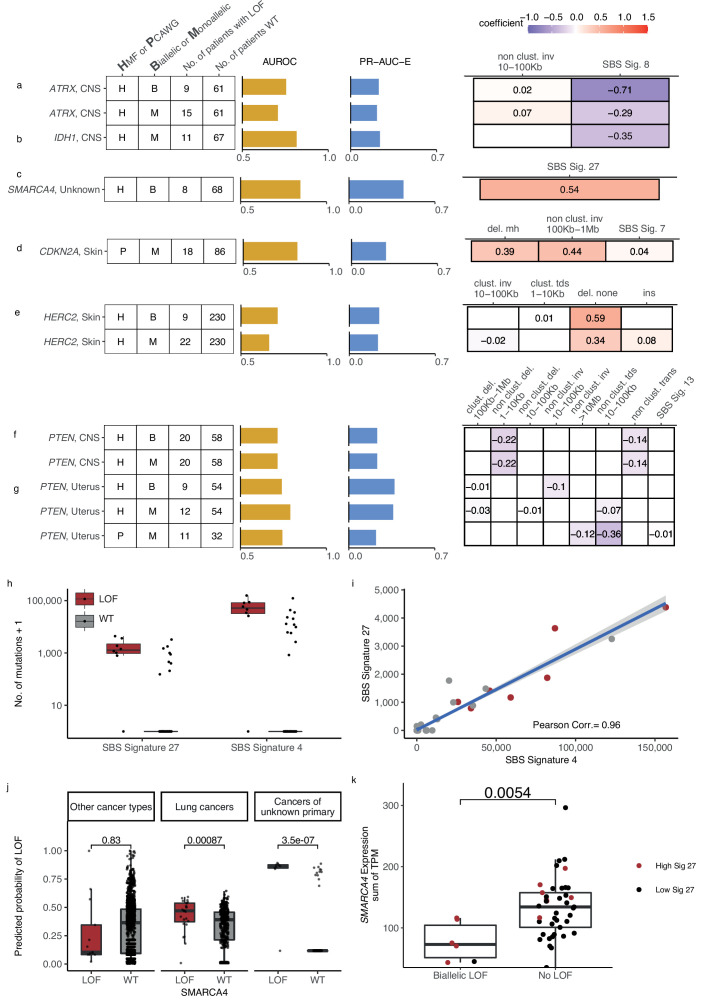
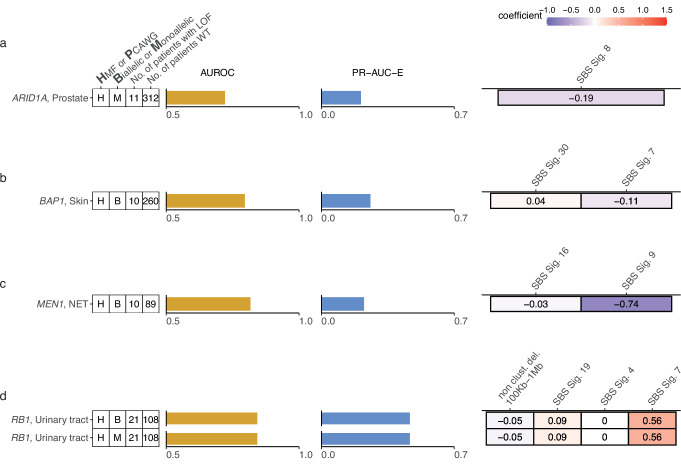
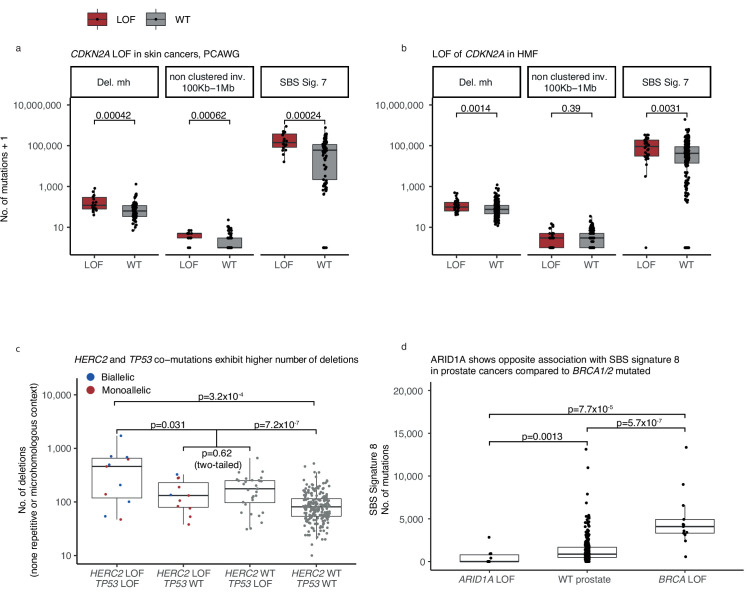
Figure 6. Novel predictive models of DNA damage response (DDR) gene deficiencies.
(a) Predictive model of ATRX-d and its PR-AUC-E, area under the receiver operator characteristic (AUROC), and selected features and their coefficients. Same information for predictive models of (b) IDH1-d, (c) SMARCA4-d, (d) CDKN2A-d, (e) HERC2-d, and (f) PTEN-d in central nervous system (CNS) cancers and (g) uterine cancers. (h) Number of single-base substitution (SBS) sig. 27 and SBS sig. 4 (y-axis; logarithmic) among tumours of unknown primary with SMARCA4 biallelic loss-of-function (LOF) (red) or wild-type (grey). (i) Pearson correlation between the per-tumour number (tumours of unknown primary; Hartwig Medical Foundation [HMF]) of SBS signature 27 (y-axis) and SBS signature 4 (x-axis; logarithmic) mutations, with an overlaid linear model (blue) and its 95% confidence interval (grey). (j) Using a model trained to predict SMARCA4 biallelic LOF in HMF cancers of unknown primary, we evaluate the predictive power across individual cohorts (one-tailed Wilcoxon rank-sum test), displaying significant cohorts separately (colours as in h). (k) Expression of SMARCA4, meassured as the sum of all annotated transcripts per milion (TPM; y-axis), for tumours with biallelic LOF and no LOF (x-axis). Colors indicate the rate of SBS sig. 27 in each tumour, (red >0; black = 0). The difference in expression was evaluated using a non-paired Wilcoxon rank-sum test.