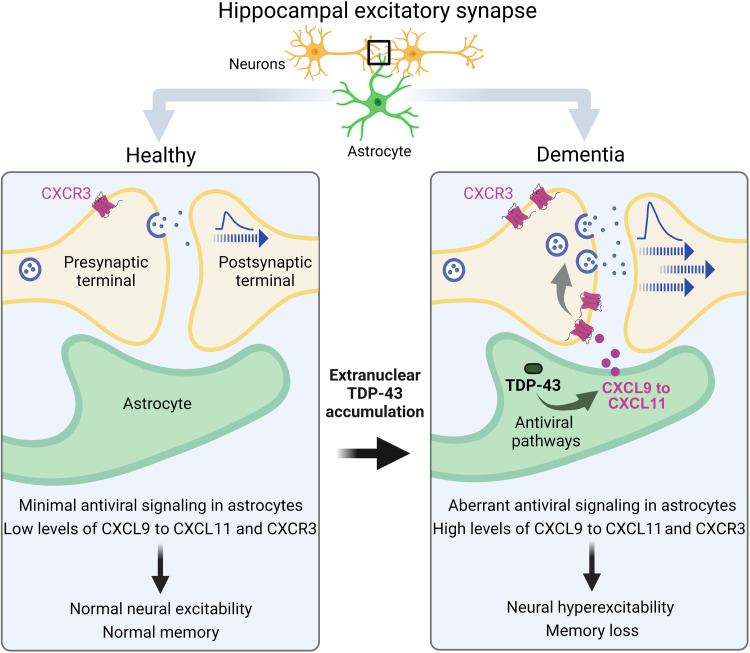
Fig. 10. Summary of the main findings.
In AD and FTD, hippocampal astrocytes had aberrant accumulation of cytoplasmic TDP-43. These alterations were linked to brain region–specific and cell-autonomous changes in astrocytic antiviral pathways and increased production of IFN-inducible chemokines. The corresponding chemokine receptor CXCR3 was increased selectively in hippocampal excitatory presynaptic terminals and promoted neuronal hyperactivity and memory loss. Thus, dementia-associated TDP-43 dysregulation in astrocytes causes chemokine-mediated changes in excitatory transmission leading to cognitive deficits.